Abstract
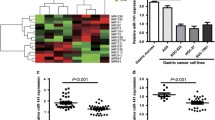
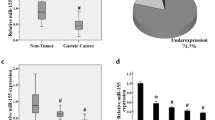
Increasing evidence shows that abnormal microRNA (miRNA) expression is involved in tumorigenesis. MiR-25 was previously reported to act as tumor suppressor or oncogene in diverse cancers. However, their expression, function, and mechanism in gastric cancer (GC) are not well known. Here, we show that miR-25 was overexpressed in primary tumor tissues of GC patients and was significantly correlated with a more aggressive phenotype of GC in patients. MiR-25 inhibition significantly decreased the proliferation, invasion, and migration of GC cells in vitro. Furthermore, miR-25 repressed F-box and WD-40 domain protein 7 (FBXW7) expression by directly binding to 3-untranslated region (UTR) of FBXW7, and the inverse correlation was observed between the expressions of miR-25 and FBXW7 mRNA in primary GC tissues. Moreover, the restoration of FBXW7 led to suppressed proliferation, invasion, and migration of GC cells. In vivo, miR-25 promotes tumor growth of GC. Taken together, miR-25 promotes GC progression by directly downregulating FBXW7 expression and may be employed as a novel prognostic marker and therapeutic target of GC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Hartgrink HH, Jansen EP, van Grieken NC, van de Velde CJ. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2009;374:477–90.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–66.
Lujambio A, Lowe SW. The microcosmos of cancer. Nature. 2012;482:347–55.
Kim YK, Yu J, Han TS, Park SY, Namkoong B, Kim DH, et al. Functional links between clustered microRNAs: suppression of cell-cycle inhibitors by microRNA clusters in gastric cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:1672–81.
Hur K, Toiyama Y, Takahashi M, Balaguer F, Nagasaka T, Koike J, et al. MicroRNA-200c modulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human colorectal cancer metastasis. Gut. 2013;62:1315–26.
Wang X, Chen X, Wang R, Xiao P, Xu Z, Chen L, et al. MicroRNA-200c modulates the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human renal cell carcinoma metastasis. Oncol Rep. 2013;30:643–50.
Wang Z, Cai Q, Jiang Z, Liu B, Zhu Z, Li C. Prognostic role of MicroRNA-21 in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2014;20:1668–74.
Han TS, Hur K, Xu G, Choi B, Okugawa Y, Toiyama Y, Oshima H, Oshima M, Lee HJ, Kim VN, Chang AN, Goel A, Yang HK. MicroRNA-29c mediates initiation of gastric carcinogenesis by directly targeting ITGB1. Gut. 2015;64:203–14.
Gong J, Li J, Wang Y, Liu C, Jia H, Jiang C, et al. Characterization of microRNA-29 family expression and investigation of their mechanistic roles in gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:497–506.
Qiao F, Zhang K, Gong P, Wang L, Hu J, Lu S, et al. Decreased miR-30b-5p expression by DNMT1 methylation regulation involved in gastric cancer metastasis. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41:5693–700.
Zhou X, Xia Y, Su J, Zhang G. Down-regulation of miR-141 induced by helicobacter pylori promotes the invasion of gastric cancer by targeting STAT4. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33:1003–12.
Li X, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Liu X, Gong T, Li M, et al. MiRNA-223 promotes gastric cancer invasion and metastasis by targeting tumor suppressor EPB41L3. Mol Cancer Res. 2011;9:824–33.
Kan T, Sato F, Ito T, Matsumura N, David S, Cheng Y, et al. The miR-106b-25 polycistron, activated by genomic amplification, functions as an oncogene by suppressing p21 and Bim. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:1689–700.
Li BS, Zuo QF, Zhao YL, Xiao B, Zhuang Y, Mao XH, Wu C, Yang SM, Zeng H, Zou QM, Guo G: MicroRNA-25 promotes gastric cancer migration, invasion and proliferation by directly targeting transducer of ERBB2, 1 and correlates with poor survival. Oncogene. 2014;34:2474–83.
Welcker M, Clurman BE. FBW7 ubiquitin ligase: a tumour suppressor at the crossroads of cell division, growth and differentiation. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:83–93.
Cheng Y, Li G. Role of the ubiquitin ligase Fbw7 in cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012;31:75–87.
Brandt Y, Mitchell T, Wu Y, Hartley RS. Developmental downregulation of Xenopus cyclin E is phosphorylation and nuclear import dependent and is mediated by ubiquitination. Dev Biol. 2011;355:65–76.
Koepp DM, Schaefer LK, Ye X, Keyomarsi K, Chu C, Harper JW, et al. Phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination of cyclin E by the SCFFbw7 ubiquitin ligase. Science. 2001;294:173–7.
Milne AN, Leguit R, Corver WE, Morsink FH, Polak M, de Leng WW, et al. Loss of CDC4/FBXW7 in gastric carcinoma. Cell Oncol. 2010;32:347–59.
Li J, Guo Y, Liang X, Sun M, Wang G, De W, et al. MicroRNA-223 functions as an oncogene in human gastric cancer by targeting FBXW7/hCdc4. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138:763–74.
Petrocca F, Visone R, Onelli MR, Shah MH, Nicoloso MS, de Martino I, et al. E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGFbeta-dependent cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:272–86.
Matuszcak C, Haier J, Hummel R, Lindner K. MicroRNAs: promising chemoresistance biomarkers in gastric cancer with diagnostic and therapeutic potential. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:13658–66.
Liu HS, Xiao HS. MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:12007–17.
Razumilava N, Bronk SF, Smoot RL, Fingas CD, Werneburg NW, Roberts LR, et al. MiR-25 targets TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) death receptor-4 and promotes apoptosis resistance in cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 2012;55:465–75.
Brett JO, Renault VM, Rafalski VA, Webb AE, Brunet A. The microRNA cluster miR-106b~25 regulates adult neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation. Aging (Albany NY). 2011;3:108–24.
Li Q, Zou C, Zou C, Han Z, Xiao H, Wei H, et al. MicroRNA-25 functions as a potential tumor suppressor in colon cancer by targeting Smad7. Cancer Lett. 2013;335:168–74.
Esposito F, Tornincasa M, Pallante P, Federico A, Borbone E, Pierantoni GM, et al. Down-regulation of the miR-25 and miR-30d contributes to the development of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma targeting the polycomb protein EZH2. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:E710–8.
Mao JH, Perez-Losada J, Wu D, Delrosario R, Tsunematsu R, Nakayama KI, et al. Fbxw7/Cdc4 is a p53-dependent, haploinsufficient tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 2004;432:775–9.
Hagedorn M, Delugin M, Abraldes I, Allain N, Belaud-Rotureau MA, Turmo M, et al. FBXW7/hCDC4 controls glioma cell proliferation in vitro and is a prognostic marker for survival in glioblastoma patients. Cell Div. 2007;2:9.
Gu Z, Inomata K, Ishizawa K, Horii A. The FBXW7 beta-form is suppressed in human glioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;354:992–8.
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Ishii H, Yokobori T, Takatsuno Y, Sato T, et al. Loss of FBXW7, a cell cycle regulating gene, in colorectal cancer: clinical significance. Int J Cancer. 2010;126:1828–37.
Lu D, Davis MP, Abreu-Goodger C, Wang W, Campos LS, Siede J, et al. MiR-25 regulates Wwp2 and Fbxw7 and promotes reprogramming of mouse fibroblast cells to iPSCs. PLoS One. 2012;7:e40938.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, J., Cui, Z., Li, L. et al. MicroRNA-25 promotes gastric cancer proliferation, invasion, and migration by directly targeting F-box and WD-40 Domain Protein 7, FBXW7. Tumor Biol. 36, 7831–7840 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3510-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3510-3