Abstract
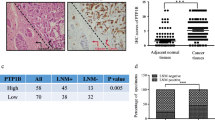
PFTK1 was a cell division cycle 2-related serine/threonine protein kinase, which was up-regulated in breast cancer tissues and breast cancer lines. And up-regulated PFTK1 was highly associated with grade, axillary lymph node status, and Ki-67. Moreover, Kaplan–Meier curve showed that up-regulated PFTK1 was related to the poor breast carcinoma patients’ overall survival. Here, we first discovered and confirmed that cyclin B was a new interacting protein of PFTK1, and the complex might increase the amount of DVL2, which triggers Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Furthermore, knockdown of PFTK1 attenuated cell proliferation, anchorage-independent cell growth, and cell migration and invasion by inhibiting the transcriptional activation of β-catenin for cyclin D1, MMP9, and HEF1, whereas exogenous expression of PFTK1 might promote MDA-MB-231 cells proliferation, migration, and invasion via promoting PFTK1–DVL2–β-catenin axis. Our findings supported the notion that up-regulated PFTK1 might promote breast cancer progression and metastasis by activating Wnt signaling pathway through the PFTK1–DVL2–β-catenin axis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sakharkar MK, Shashni B, Sharma K, Dhillon SK, Ranjekar PR, Sakharkar KR. Therapeutic implications of targeting energy metabolism in breast cancer. PPAR Res. 2013;2013:109285.
Bray F, McCarron P, Parkin DM. The changing global patterns of female breast cancer incidence and mortality. Breast Cancer Res. 2004;6(6):229–39.
Berry DA, Cronin KA, Plevritis SK, Fryback DG, Clarke L, Zelen M, et al. Effect of screening and adjuvant therapy on mortality from breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(17):1784–92.
Cooney CA, Jousheghany F, Yao-Borengasser A, Phanavanh B, Gomes T, Kieber-Emmons AM, et al. Chondroitin sulfates play a major role in breast cancer metastasis: a role for CSPG4 and CHST11 gene expression in forming surface P-selectin ligands in aggressive breast cancer cells. Breast cancer Res. 2011;13(3):R58.
Fujii S, Tokita K, Wada N, Ito K, Yamauchi C, Ito Y, et al. MEK–ERK pathway regulates EZH2 overexpression in association with aggressive breast cancer subtypes. Oncogene. 2011;30(39):4118–28.
Kong C, Wang C, Wang L, Ma M, Niu C, Sun X, et al. NEDD9 is a positive regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes invasion in aggressive breast cancer. PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22666.
Cheng GZ, Chan J, Wang Q, Zhang W, Sun CD, Wang L-H. Twist transcriptionally up-regulates AKT2 in breast cancer cells leading to increased migration, invasion, and resistance to paclitaxel. Cancer Res. 2007;67(5):1979–87.
Yee DS, Tang Y, Li X, Liu Z, Guo Y, Ghaffar S, et al. The Wnt inhibitory factor 1 restoration in prostate cancer cells was associated with reduced tumor growth, decreased capacity of cell migration and invasion and a reversal of epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:162.
Clevers H, Nusse R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell. 2012;149(6):1192–205.
Gabrovska P, Smith RA, Tiang T, Weinstein SR, Haupt LM, Griffiths LR. Development of an eight gene expression profile implicating human breast tumours of all grade. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(4):3879–92.
Khramtsov AI, Khramtsova GF, Tretiakova M, Huo D, Olopade OI, Goss KH. Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation is enriched in basal-like breast cancers and predicts poor outcome. Am J Pathol. 2010;176(6):2911–20.
Loh YN, Hedditch EL, Baker LA, Jary E, Ward RL, Ford CE. The Wnt signalling pathway is upregulated in an in vitro model of acquired tamoxifen resistant breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2013;13(1):174.
Incassati A, Chandramouli A, Eelkema R, Cowin P. Key signaling nodes in mammary gland development and cancer: beta-catenin. Breast cancer Res. 2010;12(6):213.
Staal FJ, Luis TC, Tiemessen MM. WNT signalling in the immune system: WNT is spreading its wings. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(8):581–93.
He T-C, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H, Zawel L, da Costa LT, et al. Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science. 1998;281(5382):1509–12.
Tetsu O, McCormick F. β-Catenin regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature. 1999;398(6726):422–6.
Xia D, Holla VR, Wang D, Menter DG, DuBois RN. HEF1 is a crucial mediator of the proliferative effects of prostaglandin E2 on colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010;70(2):824–31.
Zucker S, Vacirca J. Role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in colorectal cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2004;23(1–2):101–17.
Smalley MJ, Sara E, Paterson H, Naylor S, Cook D, Jayatilake H, et al. Interaction of Axin and Dvl-2 proteins regulates Dvl-2-stimulated TCF-dependent transcription. EMBO J. 1999;18(10):2823–35.
Yang T, Chen J. Identification and cellular localization of human PFTAIRE1. Gene. 2001;267(2):165–72.
Shu F, Lv S, Qin Y, Ma X, Wang X, Peng X, et al. Functional characterization of human PFTK1 as a cyclin-dependent kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2007;104(22):9248–53.
Jiang M, Gao Y, Yang T, Zhu X, Chen J. Cyclin Y, a novel membrane-associated cyclin, interacts with PFTK1. FEBS Lett. 2009;583(13):2171–8.
Leung W, Ching A, Chan A, Poon T, Mian H, Wong A, et al. A novel interplay between oncogenic PFTK1 protein kinase and tumor suppressor TAGLN2 in the control of liver cancer cell motility. Oncogene. 2011;30(44):4464–75.
Miyagaki H, Yamasaki M, Miyata H, Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y, Nakajima K, et al. Overexpression of PFTK1 predicts resistance to chemotherapy in patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2012;106(5):947–54.
Yue W, Zhao X, Zhang L, Xu S, Liu Z, Ma L, et al. Cell cycle protein cyclin Y is associated with human non-small-cell lung cancer proliferation and tumorigenesis. Clin Lung Cancer. 2011;12(1):43–50.
Sun T, Co NN, Wong N. PFTK1 interacts with cyclin Y to activate non-canonical Wnt signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;449(1):163–8.
Niehrs C, Acebron SP. Mitotic and mitogenic Wnt signalling. EMBO J. 2012;31(12):2705–13.
Liu Y, Wang Y, Cheng C, Chen Y, Shi S, Qin J, et al. A relationship between p27kip1 and Skp2 after adult brain injury: implications for glial proliferation. J Neurotrauma. 2010;27(2):361–71.
Ji L, Li H, Gao P, Shang G, Zhang DD, Zhang N, et al. Nrf2 pathway regulates multidrug-resistance-associated protein 1 in small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e63404.
Tao T, Cheng C, Ji Y, Xu G, Zhang J, Zhang L, et al. Numbl inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion by suppressing TRAF5-mediated NF-κB activation. Mol Biol Cell. 2012;23(14):2635–44.
Liu Z, Rebowe RE, Wang Z, Li Y, Wang Z, DePaolo JS, et al. KIF3a promotes proliferation and invasion via Wnt signaling in advanced prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2014;12(4):491–503.
Dai M, Al-Odaini AA, Fils-Aimé N, Villatoro MA, Guo J, Arakelian A, et al. Cyclin D1 cooperates with p21 to regulate TGFb-mediated breast cancer cell migration and tumor local invasion. Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(3):R49.
Marastoni S, Andreuzzi E, Paulitti A, Colladel R, Pellicani R, Todaro F, et al. EMILIN2 down-modulates the Wnt signalling pathway and suppresses breast cancer cell growth and migration. J Pathol. 2014;232(4):391–404.
Prasad CP, Chaurasiya SK, Axelsson L, Andersson T. WNT-5A triggers Cdc42 activation leading to an ERK1/2 dependent decrease in MMP9 activity and invasive migration of breast cancer cells. Mol Oncol. 2013;7(5):870–83.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grants (Nos. 81302285, 81472185).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xiaoling Gu and Yingying Wang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, X., Wang, Y., Wang, H. et al. Upregulated PFTK1 promotes tumor cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in breast cancer. Med Oncol 32, 195 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0641-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0641-8