Abstract
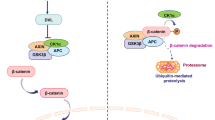
β-Catenin, a core component of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, has been shown to be a crucial factor in a broad range of tumors, while its role in glioma is not well understood. In this study, the expression of β-catenin in astrocytic glioma tissues with different grade and human normal cerebral tissues was examined using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and immunohistochemistry. We found a higher expression level of β-catenin in astrocytic glioma patients with high grade in comparison with the normal controls. Additionally, siRNA was transfected into human U251 glioblastoma cells by liposome after the design of siRNA was confirmed to effectively inhibit the expression of β-catenin by RT-PCR. Compared to the control siRNA group, siRNA-mediated knockdown of β-catenin in human U251 cells inhibited cell proliferation, resulted in cell apoptosis, and arrested cell cycle in G 0/G 1. Additionally, downregulation of β-catenin decreased the expression level of cyclin D1, c-Myc and c-jun. Taken together, these results indicate that overexpression of β-catenin may be an important contributing factor to glioma progression.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peifer M, Polakis P. Wnt signaling in oncogenesis and embryogenesis-a look outside the nucleus. Science. 2000;287:1606–9.
Fodde R, Brabletz T. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cancer stemness and malignant behavior. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19:150–8.
Polakis P. Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev. 2000;14:1837–51.
Barker N. The canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;468:5–15.
Simon M, Grandage VL, Linch DC, Khwaja A. Constitutive activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway in acute myeloid leukaemia. Oncogene. 2005;24:2410–20.
Gavert N, Ben-Ze’ev A. Beta-catenin signaling in biological control and cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2007;102:820–8.
Dihlmann S, von Knebel Doeberitz M. Wnt/beta-catenin-pathway as a molecular target for future anti-cancer therapeutics. Int J Cancer. 2005;113:515–24.
Karim R, Tse G, Putti T, Scolyer R, Lee S. The significance of the Wnt pathway in the pathology of human cancers. Pathology. 2004;36:120–8.
Hatsell S, Rowlands T, Hiremath M, Cowin P. Beta-catenin and Tcfs in mammary development and cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2003;8:145–58.
Mann B, et al. Target genes of β-catenin-T cell-factor/lymphoidenhancer-factor signaling in human colorectal carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:1603–8.
Rowlands TM, Pechenkina IV, Hatsell S, Cowin P. Beta-catenin and cyclin D1: connecting development to breast cancer. Cell Cycle. 2004;3:145–8.
Pu P, et al. Downregulation of Wnt2 and beta-catenin by siRNA suppresses malignant glioma cell growth. Cancer Gene Ther. 2009;16:351–61.
Sareddy GR, Panigrahi M, Challa S, Mahadevan A, Babu PP. Activation of Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling pathway in human astrocytomas. Neurochem Int. 2009;55:307–17.
Liu X, et al. Overexpression of an isoform of AML1 in acute leukemia and its potential role in leukemogenesis. Leukemia. 2009;23:739–45.
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Weber K, Tuschl T. Analysis of gene function in somatic mammalian cells using a small interference RNAs. Methods. 2002;26:199–213.
Müller T, Choidas A, Reichmann E, Ullrich A. Phosphorylation and free pool of beta-catenin are regulated by tyrosine kinases and tyrosine phosphatases during epithelial cell migration. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:10173–83.
Utsuki S, et al. Relationship between the expression of E-, N-cadherins and beta-catenin and tumor grade in astrocytomas. J Neurooncol. 2002;57:187–92.
Sareddy GR, Challa S, Panigrahi M, Babu PP. Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling pathway activation in malignant progression of rat gliomas induced by transplacental N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea exposure. Neurochem Res. 2009;34:1278–88.
Kim JK, Diehl JA. Nuclear cyclin D1: an oncogenic driver in human cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2009;220:292–6.
Dang CV, et al. The c-Myc target gene network. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006;16:253–64.
Saadeddin A, Babaei-Jadidi R, Spencer-Dene B, Nateri AS. The links between transcription, beta-catenin/JNK signaling, and carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7:1189–96.
Takayama S, Rogatsky I, Schwarcz LE, Darimont BD. The glucocorticoid receptor represses cyclin D1 by targeting the TCF/beta-catenin complex. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:17856–63.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Prof. Qing Rao and Prof. Min Wang (Institute of Hematology and Blood Disease Hospital, China) for technical support. This work was supported by Postdoctoral Science Found (20080440423) of China and Clinical and Basic Cooperation Fund of Capital University of Medical Sciences (2006JL36).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiangrong Liu and Lei Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Wang, L., Zhao, S. et al. β-Catenin overexpression in malignant glioma and its role in proliferation and apoptosis in glioblastma cells. Med Oncol 28, 608–614 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9476-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9476-5