Abstract
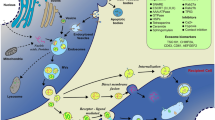
Exosomes are vesicles, ranging of 30–150 nm in diameter, which are released by different cell types into the extracellular space. Exosomes are capable of transporting several biomolecules such as proteins, lipids, DNA, mRNA, and non-coding RNA, including microRNAs (miRs). miRs signatures have been linked to the development of non-communicable diseases and their classification into various subtypes and/or stages. Interestingly, the miRs contained in exosomes (exomiRs) are suitable candidates as non-invasive biomarkers due to their stability in body fluids and harsh conditions, as well as they are considered critical players involved in intercellular communication; so that they can be a promising diagnostic tool for several diseases. Besides, exomiRs allow discrimination between different stages of the disease and could be a valuable strategy for the early detection of several pathologies in a non-invasive approach. This review aims to describe exomiRs present in biologic fluids that can be used as a tool for the diagnosis and prognosis of non-communicable diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular, kidney, and neurodegenerative disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brennan K et al (2020) A comparison of methods for the isolation and separation of extracellular vesicles from protein and lipid particles in human serum. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-57497-7
Doyle LM, Wang MZ (2019) Overview of extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells:41–68. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070727
Console L, Scalise M, Indiveri C (2019) Exosomes in inflammation and role as biomarkers. Clin Chim Acta 488(2018):165–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2018.11.009
Gibbings DJ, Ciaudo C, Erhardt M, Voinnet O (2009) Multivesicular bodies associate with components of miRNA effector complexes and modulate miRNA activity. Nat Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1929
Shurtleff MJ, Temoche-Diaz MM, Karfilis KV, Ri S, Schekman R (2016) Y-box protein 1 is required to sort microRNAs into exosomes in cells and in a cell-free reaction. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.19276
Minciacchi VR et al (2016) The emerging role of large Oncosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol:41–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.02.010.Extracellular
Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR, Soleymani Fard S, Ghaffari SH (2019) An overview of microRNAs: biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell Physiol 234(5):5451–5465. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27486
Salido-Guadarrama I, Romero-Cordoba S, Peralta-Zaragoza O, Hidalgo-Miranda A, Rodríguez-Dorantes M (2014) MicroRNAs transported by exosomes in body fluids as mediators of intercellular communication in cancer. Onco Targets Ther 7:1327–1338. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S61562
Bhome R et al (2018) Exosomal microRNAs (exomiRs): small molecules with a big role in cancer. Cancer Lett 420:228–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.02.002
Bertoli G, Cava C, Castiglioni I (2015) Micrornas: new biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, therapy prediction and therapeutic tools for breast cancer. Theranostics. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.11543
WHO (2018) Latest global cancer data: Cancer burden rises to 18.1 million new cases and 9.6 million cancer deaths in 2018. pp 13–15
Hannafon BN, Ding WQ (2013) Intercellular communication by exosome-derived microRNAs in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 14(7):14240–14269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140714240
Roma-Rodrigues C, Fernandes AR, Baptista PV (2014) Exosome in tumour microenvironment: overview of the crosstalk between normal and cancer cells. Biomed Res Int 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/179486
Min L et al (2019) Loss of circulating exosomal miR-92b is a novel biomarker of colorectal cancer at early stage. Int J Med Sci 16(9):1231–1237. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.34540
Takano Y et al (2017) Circulating exosomal microRNA-203 is associated with metastasis possibly via inducing tumor-associated macrophages in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 8(45):78598–78613. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20009
Liu X et al (2018) Circulating exosomal miR-27a and miR-130a act as novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of colorectal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 27(7):746–754. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-18-0067
Eichelser C et al (2014) Increased serum levels of circulating exosomal microRNA-373 in receptor-negative breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 5(20):9650–9663. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2520
Goto T et al (2018) An elevated expression of serum exosomal microRNA-191, − 21, −451a of pancreatic neoplasm is considered to be efficient diagnostic marker. BMC Cancer 18(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4006-5
Yokoi A et al (2018) Integrated extracellular microRNA profiling for ovarian cancer screening. Nat Commun 9(1):2–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06434-4
Samsonov R et al (2016) Lectin-induced agglutination method of urinary exosomes isolation followed by mi-RNA analysis: application for prostate cancer diagnostic. Prostate 76(1):68–79. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.23101
WHO (2014) Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014. Geneva
Anand S (2013) A brief primer on microRNAs and their roles in angiogenesis. Vasc Cell 5(1):2. https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-824X-5-2
Feinberg MW, Moore KJ (2016) MicroRNA regulation of atherosclerosis. Circ Res 118(4):703–720. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306300
Kumar S, Williams D, Sur S, Wang J-Y, Jo H (2019) Role of flow-sensitive microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in vascular dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Vasc Pharmacol 114:76–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vph.2018.10.001
Santovito D et al (2013) Overexpression of microRNA-145 in atherosclerotic plaques from hypertensive patients. Expert Opin Ther Targets 17(3):217–223. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728222.2013.745512
Wu Q, Yuan X, Li B, Han R, Zhang H, Xiu R (2020) Integrated exosomal miRNA and transcriptome analysis of brain microvascular endothelial cells in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertens Res 43(2):90–98. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-019-0345-0
Jayaseelan VP, Arumugam P (2020) Exosomal microRNAs as a promising theragnostic tool for essential hypertension. Hypertens Res 43(1):74–75. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-019-0343-2
Wong L, Wang J, Liew O, Richards A, Chen Y-T (2016) MicroRNA and heart failure. Int J Mol Sci 17(4):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040502
Qiao L et al (2019) microRNA-21-5p dysregulation in exosomes derived from heart failure patients impairs regenerative potential. J Clin Invest 129(6):2237–2250. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI123135
Wu T et al (2018) Circulating exosomal miR-92b-5p is a promising diagnostic biomarker of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction patients hospitalized for acute heart failure. J Thorac Dis 10(11):6211–6220. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2018.10.52
Jairajpuri DS, Malalla ZH, Mahmood N, Almawi WY (2017) Circulating microRNA expression as predictor of preeclampsia and its severity. Gene 627:543–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.07.010
Wang Y et al (2019) Serum Exosomal microRNA let-7i-3p as candidate diagnostic biomarker for Kawasaki disease patients with coronary artery aneurysm. IUBMB Life:iub.2015. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.2015
Lan H, Chung A, Yu X (2013) MicroRNA and nephropathy: emerging concepts. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis:169. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJNRD.S37885
Sonoda H et al (2019) miRNA profiling of urinary exosomes to assess the progression of acute kidney injury. Sci Rep 9(1):4692. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40747-8
Du J et al (2013) MicroRNA-21 and risk of severe acute kidney injury and poor outcomes after adult cardiac surgery. PLoS One 8(5):e63390. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063390
Zhou P, Chen Z, Zou Y, Wan X (2016) Roles of non-coding RNAs in acute kidney injury. Kidney Blood Press Res 41(6):757–769. https://doi.org/10.1159/000450566
Umanath K, Lewis JB (2018) Update on diabetic nephropathy: Core curriculum 2018. Am J Kidney Dis 71(6):884–895. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.10.026
Eissa S, Matboli M, Bekhet MM (2016) Clinical verification of a novel urinary microRNA panal: 133b, −342 and −30 as biomarkers for diabetic nephropathy identified by bioinformatics analysis. Biomed Pharmacother 83:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.06.018
Beltrami C et al (2018) Association of Elevated Urinary miR-126, miR-155, and miR-29b with diabetic kidney disease. Am J Pathol 188(9):1982–1992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.06.006
Zang J, Maxwell AP, Simpson DA, McKay GJ (2019) Differential expression of urinary Exosomal MicroRNAs miR-21-5p and miR-30b-5p in individuals with diabetic kidney disease. Sci Rep 9(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-47504-x
Delić D et al (2016) Urinary exosomal miRNA signature in type II diabetic nephropathy patients. PLoS One 11(3):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0150154
Chen T et al (2019) Increased urinary exosomal microRNAs in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. EBioMedicine 39:552–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.11.018
Cao DD, Li L, Chan WY (2016) MicroRNAs: key regulators in the central nervous system and their implication in neurological diseases. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060842
Fabbri M (2018) MicroRNAs and mirceptors: a new mechanism of action for intercellular communication. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2016.0486
De Toro J, Herschlik L, Waldner C, Mongini C (2015) Emerging roles of exosomes in normal and pathological conditions: new insights for diagnosis and therapeutic applications. Front Immunol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00203
Lehmann SM et al (2012) An unconventional role for miRNA: Let-7 activates toll-like receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3113
Lugli G et al (2015) Plasma exosomal miRNAs in persons with and without Alzheimer disease: altered expression and prospects for biomarkers. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139233
Gui Y, Liu H, Zhang L, Lv W, Hu X (2015) Altered microRNA profiles in cerebrospinal fluid exosome in Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease. Oncotarget
Margis R, Margis R, Rieder CRM (2011) Identification of blood microRNAs associated to Parkinsonós disease. J Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.01.023
Cao XY et al (2017) MicroRNA biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease in serum exosome-like microvesicles. Neurosci Lett. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.02.045
Ebrahimkhani S et al (2017) Exosomal microRNA signatures in multiple sclerosis reflect disease status. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14301-3
Xu YF, Hannafon BN, Zhao YD, Postier RG, Ding WQ (2017) Plasma exosome miR-196a and miR-1246 are potential indicators of localized pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 8(44):77028–77040. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20332
Huang X (2015) Exosomal miR-1290 and miR-375 as prognostic markers in castration-resistant prostate Cancer. Eur Urol 67(1):33–41. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.956839
Meng X, Müller V, Milde-langosch K, Trillsch F, Schwarzenbach H (2016) Diagnostic and prognostic relevance of circulating exosomal miR-373 , miR-200a , miR-200b and miR-200c in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. 7(13)
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Yin Y, Li S (2019) Detection of circulating exosomal miR-17-5p serves as a novel non-invasive diagnostic marker for non-small cell lung cancer patients. Pathol Res Pract 215(8):152466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2019.152466
Nakano T et al (2019) Circulating exosomal miR-92b: its role for cancer immunoediting and clinical value for prediction of posttransplant hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. Am J Transplant:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.15490
Gonzalez-Villasana V et al (2019) Presence of circulating miR-145, miR-155, and miR-382 in exosomes isolated from serum of breast Cancer patients and healthy donors. Dis Markers 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6852917
Fu F, Jiang W, Zhou L, Chen Z (2018) Circulating Exosomal miR-17-5p and miR-92a-3p predict pathologic stage and grade of colorectal Cancer. Transl Oncol 11(2):221–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2017.12.012
Meltzer S et al (2019) Circulating Exosomal miR-141-3p and miR-375 in metastatic progression of rectal Cancer. Transl Oncol 12(8):1038–1044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2019.04.014
Zheng M et al (2019) Exosomal let-7d-3p and miR-30d-5p as diagnostic biomarkers for non-invasive screening of cervical cancer and its precursors. Mol Cancer 18(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0999-x
Acknowledgements
The Posdoctoral fellowship awarded CVU (417965) by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT), Mexico. Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT) (FOSEC-SS/IMSS/ISSSTE A3-S-43439).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JAJ-A: writing neurodegenerative disease section and conceptualization (lead). JCF-M: writing renal and cardiovascular disease sections, review and editing (equal). AKG-P: conceptualization (equal), writing cancer section, original draft (supporting), review and editing (lead).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiménez-Avalos, J.A., Fernández-Macías, J.C. & González-Palomo, A.K. Circulating exosomal MicroRNAs: New non-invasive biomarkers of non-communicable disease. Mol Biol Rep 48, 961–967 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-06050-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-06050-w