Abstract
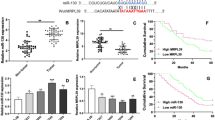
In human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), miR-34a was downregulated and could inhibit in vitro cell proliferation and migration. However, the underlying mechanism was not clear yet. The expression levels of mRNA and protein were detected by quantitative real-time PCR or western blotting, respectively. MiR-34a was knocked down or overexpressed and transfected into human ESCC cell lines ECA109 and TE-13, respectively. Cell migration and wound healing assays were used to examine the effect on migration and invasion in vitro. Animal models were used to examine the role of miR-34a in metastasis in vivo. Luciferase assay was carried out to validate the potential target of miR-34a. CD44 was upregulated and miR-34a was downregulated in ESCC tissues and cell lines. The linear regression analysis showed that CD44 expression was negatively correlated with the level of miR-34a. Luciferase assay showed that miR-34a interacted with a putative binding site in the CD44 3′UTR. MiR-34a was found to negatively regulate the expression of CD44. In vitro experiment showed that miR-34a overexpression inhibited ESCC cell invasion and migration; whereas miR-34a knockdown showed reversed results. MiR-34a also inhibited esophagus tumor growth and metastasis in vivo; whereas miR-34a knockdown showed reversed results. Finally, we found that CD44 knockdown reversed the effects of miR-34a knockdown on ESCC cell invasion and migration in vitro. MiRNA-34a suppresses invasion and metastatic in ESCC by regulating CD44.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold M, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J, Forman D (2015) Global incidence of oesophageal cancer by histological subtype in 2012. Gut 64:381
Lagergren J (2015) Oesophageal cancer in 2014: advances in curatively intended treatment. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 12:74–75
Li B, Xu WW, Han L, Chan KT, Tsao SW, Lee NP, Law S, Xu LY, Li EM, Chan KW (2017) MicroRNA-377 suppresses initiation and progression of esophageal cancer by inhibiting CD133 and VEGF. Oncogene 36(28):3986–4000
Calin GA, Croce CM (2006) MicroRNA-cancer connection: the beginning of a new tale. Can Res 66:7390–7394
Yu T, Liu K, Wu Y, Fan J, Chen J, Li C, Yang Q, Wang Z (2013) MicroRNA-9 inhibits the proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by suppressing expression of CXCR4 via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncogene 33(42):5017–5027
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Aqeilan RI, Zupo S, Dono M (2005) miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13944–13949
Si M, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F, Mo Y (2007) miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene 26:2799–2803
Cho WC, Chow AS, Au JS (2009) Restoration of tumour suppressor hsa-miR-145 inhibits cancer cell growth in lung adenocarcinoma patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Eur J Cancer 45:2197–2206
He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan Z, Liang Y, Xue W, Zender L, Magnus J, Ridzon D, Jackson AL, Linsley PS, Chen C, Lowe SW, Cleary MA, Hannon GJ (2007) A microRNA component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature 447:1130–1134. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05939
Lodygin D, Tarasov V, Epanchintsev A, Berking C, Knyazeva T, Körner H, Knyazev P, Diebold J, Hermeking H (2008) Inactivation of miR-34a by aberrant CpG methylation in multiple types of cancer. Cell Cycle 7:2591
Ma Y, Qin H, Cui Y (2013) MiR-34a targets GAS1 to promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis in papillary thyroid carcinoma via PI3 K/Akt/Bad pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 441:958–963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.11.010
Lin X, Xu XY, Chen QS, Huang C (2015) Clinical significance of microRNA-34a in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Genet Mol Res Gmr 14:17684
Hu Y, Correa AM, Hoque A, Guan B, Ye F, Huang J, Swisher SG, Wu TT, Ajani JA, Xu XC (2011) Prognostic significance of differentially expressed miRNAs in esophageal cancer. Int J Cancer 128:132–143
Li J, Wang K, Chen X, Meng H, Song M, Wang Y, Xu X, Bai Y (2012) Transcriptional activation of microRNA-34a by NF-kappa B in human esophageal cancer cells. BMC Mol Biol 13:4
Shi H, Zhou S, Liu J, Zhu J, Xue J, Gu L, Chen Y (2016) miR-34a inhibits the in vitro cell proliferation and migration in human esophageal cancer. Pathol Res Pract 212:444–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2016.02.019
Zhao H, Ma B, Wang Y, Han T, Zheng L, Sun C, Liu T, Zhang Y, Qiu X, Fan Q (2013) miR-34a inhibits the metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by repressing the expression of CD44. Oncol Rep 29:1027–1036
Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M, Underhill CB, Seed B (1990) CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell 61:1303
Ponta H, Sherman L, Herrlich PA (2003) CD44: from adhesion molecules to signalling regulators. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:33
Marhaba R, Zöller M (2004) CD44 in cancer progression: adhesion, migration and growth regulation. J Mol Histol 35:211–231
Olsson E, Honeth G, Bendahl P, Lao HS, Gruvbergersaal S, Ringnér M, Vallonchristersson J, Jönsson G, Holm K, Lövgren K (2011) CD44 isoforms are heterogeneously expressed in breast cancer and correlate with tumor subtypes and cancer stem cell markers. BMC Cancer 11:418
Heyse TJ, Malcherczyk D, Moll R, Timmesfeld N, Wapelhorst J, Fuchs-Winkelmann S, Paletta JR, Schofer MD (2010) CD44: survival and metastasis in chondrosarcoma. Osteoarthr Cartil 18:849–856
Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, Xin C, Calhoundavis T, Li H, Patrawala L, Hong Y, Jeter C, Honorio S (2011) The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med 186:211
Shi Y, Liu C, Liu X, Tang DG, Wang J (2014) The microRNA miR-34a inhibits non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) growth and the CD44hi stem-like NSCLC cells. PLoS ONE 9:e90022
Gan Y, Yao W, Wei X, Li H, Hua X, Lang B (2014) MicroRNA-34a functions as an anti-metastatic microRNA and suppresses angiogenesis in bladder cancer by directly targeting CD44. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 33:779
Nie J, Ge X, Geng Y, Cao H, Zhu W, Jiao Y, Wu J, Zhou J, Cao J (2015) miR-34a inhibits the migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting Yin Yang-1. Oncol Rep 34:311
Li N, Fu H, Tie Y, Hu Z, Kong W, Wu Y, Zheng X (2009) miR-34a inhibits migration and invasion by down-regulation of c-Met expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 275(1):44–53
Jia L, Wei S, Mitchelson K, Gao Y, Zheng Y, Meng Z, Gan Y, Yu G (2014) miR-34a inhibits migration and invasion of tongue squamous cell carcinoma via targeting MMP9 and MMP14. PLoS ONE 9:e108435
Lai M, Du G, Shi R, Yao J, Yang G, Wei Y, Zhang D, Xu Z, Zhang R, Li Y (2015) miR-34a inhibits migration and invasion by regulating the SIRT1/p53 pathway in human SW480 cells. Mol Med Rep 11:3301–3307
Atala A (2011) Re: the MicroRNA miR-34a Inhibits Prostate Cancer Stem Cells and Metastasis by Directly Repressing CD44. J Urol 17:211
Gaur S (2014) The Role of MIR-34a in inhibition of prostate tumor growth in the bone and Induction of Autophagy. UT GSBS Dissertations and Theses. Paper 523
Jing YK, Wei W, Huynh HD, Jin Z, Wang X, Chang TC, Xie X, He L, Mangala LS, Lopezberestein G (2015) Abstract P6-17-01: MicroRNA-34a suppresses breast cancer bone metastasis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and targeting tgif2. Cancer Res 75:P6-17-01-P6-17-01
Xiao X, Huang X, Ye F, Chen B, Song C, Wen J, Zhang Z, Zheng G, Tang H, Xie X (2016) The miR-34a-LDHA axis regulates glucose metabolism and tumor growth in breast cancer. Sci Rep 6:21735
Yan K, Gao J, Yang T, Ma Q, Qiu X, Fan Q, Ma B (2012) MicroRNA-34a inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells both in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 7:e33778
Zhao Y, Tu MJ, Wang WP, Qiu JX, Yu AX, Yu AM (2016) Genetically engineered pre-microRNA-34a prodrug suppresses orthotopic osteosarcoma xenograft tumor growth via the induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Sci Rep 6:26611
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.035
Sun F, Fu H, Liu Q, Tie Y, Zhu J, Xing R, Sun Z, Zheng X (2008) Downregulation of CCND1 and CDK6 by miR-34a induces cell cycle arrest. FEBS Lett 582:1564–1568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2008.03.057
Wei JS, Song YK, Durinck S, Chen QR, Cheuk AT, Tsang P, Zhang Q, Thiele CJ, Slack A, Shohet J, Khan J (2008) The MYCN oncogene is a direct target of miR-34a. Oncogene 27:5204–5213. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.154
Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M, Lowenstein CJ (2008) miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:13421–13426. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0801613105
Yu G, Li H, Wang J, Gumireddy K, Li A, Yao W, Tang K, Xiao W, Hu J, Xiao H (2014) miRNA-34a suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting CD44 in human renal carcinoma cells. J Urol 192:1229–1237
Li H, Yu G, Shi R, Lang B, Chen X, Xia D, Xiao H, Guo X, Guan W, Ye Z (2014) Cisplatin-induced epigenetic activation of miR-34a sensitizes bladder cancer cells to chemotherapy. Mol Cancer 13:8
Louderbough JM, Schroeder JA (2011) Understanding the dual nature of CD44 in breast cancer progression. Mol Cancer Res 9:1573–1586. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.mcr-11-0156
Su YJ, Lai HM, Chang YW, Chen GY, Lee JL (2011) Direct reprogramming of stem cell properties in colon cancer cells by CD44. EMBO J 30:3186–3199. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2011.211
Li C, Lee CJ, Simeone DM (2009) Identification of human pancreatic cancer stem cells. Methods Mol Biol 568:161–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-280-9_10
Palapattu GS, Wu C, Silvers CR, Martin HB, Williams K, Salamone L, Bushnell T, Huang LS, Yang Q, Huang J (2009) Selective expression of CD44, a putative prostate cancer stem cell marker, in neuroendocrine tumor cells of human prostate cancer. Prostate 69:787–798. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.20928
Chen W, Zhang X, Chu C, Cheung WL, Ng L, Lam S, Chow A, Lau T, Chen M, Li Y, Nie Y, Wong BC, Pang R (2013) Identification of CD44 + cancer stem cells in human gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 60:949–954. https://doi.org/10.5754/hge12881
Hu B, Luo W, Hu RT, Zhou Y, Qin SY, Jiang HX (2015) Meta-analysis of prognostic and clinical significance of CD44v6 in esophageal cancer. Medicine 94:e1238
Fujiwara Y, Yoshikawa R, Tsujie M, Kato H, Takeyama H, Kitani K, Yukawa M and Inoue M (2015) CD44, a cancer stemness marker, to predict poor clinical outcome of esophageal cancer patients after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. http://meeting.ascopubs.org/cgi/content/abstract/33/15_suppl/e15068
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, J., Zhu, K., Wang, Y. et al. MicroRNA-34a suppresses invasion and metastatic in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating CD44. Mol Cell Biochem 443, 139–149 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3218-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3218-3