Abstract
Background
Circular RNA (circRNA) tubulin gamma complex associated protein 3 (circTUBGCP3) has been reported to play an oncogenic role in colorectal cancer and osteosarcoma.
Aims
We further assessed the role and working mechanism of circTUBGCP3 in rectal cancer progression.
Methods
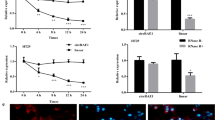
Colony formation assay and transwell assays were performed to analyze cell colony formation ability and motility. Flow cytometry was utilized to assess cell cycle progression and cell apoptosis. The production of lactate and the consumption of glucose were evaluated by fluorescence-based glucose/lactate assay kit to analyze cell glycolysis. The intermolecular interaction was verified by dual-luciferase reporter assay. In vivo experiments were carried out to analyze the role of circTUBGCP3 in tumor growth using xenograft tumor model.
Results
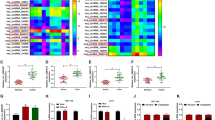
CircTUBGCP3 was significantly up-regulated in rectal cancer tissues and cell lines. CircTUBGCP3 interference inhibited the colony formation ability, migration, invasion, cell cycle progression, and glycolysis and promoted the apoptosis in rectal cancer cells. CircTUBGCP3 negative regulated microRNA-375 (miR-375) expression through interacting with it and circTUBGCP3 silencing-mediated effects in rectal cancer cells were largely based on the up-regulation of miR-375. Rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinase 1 (ROCK1) was a target of miR-375, and ROCK1 was regulated by circTUBGCP3/miR-375 axis in rectal cancer cells. MiR-375 overexpression suppressed the malignant behaviors of rectal cancer cells partly through down-regulating ROCK1. CircTUBGCP3 interference restrained rectal cancer progression in vivo.
Conclusion
CircTUBGCP3 acted as an oncogene to promote the malignant phenotypes of rectal cancer cells by modulating miR-375/ROCK1 axis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The analyzed data sets generated during the present study are available from the corresponding authors (Chao Li and Xiaosong Gu) on reasonable request.
References
Bailey CE, Hu CY, You YN et al. Increasing disparities in the age-related incidences of colon and rectal cancers in the United States, 1975–2010. JAMA Surg 2015;150:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2014.1756.
Conde-Muíño R, Cuadros M, Zambudio N et al. Predictive Biomarkers to Chemoradiation in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Biomed Res Int 2015;2015:921435. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/921435.
Du D, Su Z, Wang D et al. Optimal Interval to Surgery After Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Rectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin Colorectal Cancer 2018;17:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clcc.2017.10.012.
Lasda E, Parker R. Circular RNAs: diversity of form and function. Rna 2014;20:1829–1842. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.047126.114.
Xian ZY, Hu B, Wang T et al. CircABCB10 silencing inhibits the cell ferroptosis and apoptosis by regulating the miR-326/CCL5 axis in rectal cancer. Neoplasma 2020;67:1063–1073. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2020_191024N1084.
Fan M, Wang Y, Gao S. Circular RNA circMTO1 acts as an antitumor factor in rectal cancer cell lines by downregulation of miR-19b-3p. J Cell Biochem. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29570.
Wang Y, Wang H, Zhang J et al. Circ_0007031 Serves as a Sponge of miR-760 to Regulate the Growth and Chemoradiotherapy Resistance of Colorectal Cancer via Regulating DCP1A. Cancer Manag Res 2020;12:8465–8479. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.s254815.
He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 2004;5:522–531. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1379.
Zhao Q, Liu Y, Wang T et al. MiR-375 inhibits the stemness of breast cancer cells by blocking the JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Eur J Pharmacol 2020;884:173359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173359.
Li L, Jia L, Ding Y. Upregulation of miR-375 inhibits human liver cancer cell growth by modulating cell proliferation and apoptosis via targeting ErbB2. Oncol Lett 2018;16:3319–3326. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.9011.
Liu XH, Wang J, Dong YH. The inhibitory effect of miR-375 targeting sp1 in colorectal cancer cell proliferation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2018;22:405–411. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201801_14188
Xu X, Chen X, Xu M, et al. miR-375–3p suppresses tumorigenesis and partially reverses chemoresistance by targeting YAP1 and SP1 in colorectal cancer cells. Aging (Albany NY) 2019;11:7357–7385. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102214
Lock FE, Ryan KR, Poulter NS et al. Differential regulation of adhesion complex turnover by ROCK1 and ROCK2. PLoS One 2012;7:e31423. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031423.
Madaule P, Furuyashiki T, Eda M et al. Citron, a Rho target that affects contractility during cytokinesis. Microsc Res Tech 2000;49:123–126. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0029(20000415)49:2%3c123::aid-jemt3%3e3.0.co;2-r.
Narumiya S, Tanji M, Ishizaki T. Rho signaling, ROCK and mDia1, in transformation, metastasis and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2009;28:65–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-008-9170-7.
Wilkinson S, Paterson HF, Marshall CJ. Cdc42-MRCK and Rho-ROCK signalling cooperate in myosin phosphorylation and cell invasion. Nat Cell Biol 2005;7:255–261. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1230.
Cai SD, Chen JS, Xi ZW et al. MicroRNA-144 inhibits migration and proliferation in rectal cancer by downregulating ROCK-1. Mol Med Rep 2015;12:7396–7402. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.4391.
Panda AC. Circular RNAs Act as miRNA Sponges. Adv Exp Med Biol 2018;1087:67–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1426-1_6.
Yin Y, Long J, He Q et al. Emerging roles of circRNA in formation and progression of cancer. J Cancer 2019;10:5015–5021. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.30828.
Li Y, Zang H, Zhang X et al. circ_0136666 Facilitates the Progression of Colorectal Cancer via miR-383/CREB1 Axis. Cancer Manag Res 2020;12:6795–6806. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.s251952.
Shen T, Cheng X, Liu X et al. Circ_0026344 restrains metastasis of human colorectal cancer cells via miR-183. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 2019;47:4038–4045. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1669620.
Xu Y, Yao T, Huang K et al. Circular RNA circTUBGCP3 Is Up-Regulated and Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration and Survivability via Sponge mir-30b in Osteosarcoma. Onco Targets Ther 2020;13:3729–3737. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s245366.
Bi J, Liu H, Cai Z, et al. Circ-BPTF promotes bladder cancer progression and recurrence through the miR-31–5p/RAB27A axis. Aging (Albany NY) 2018;10:1964–1976. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101520
Liang HF, Zhang XZ, Liu BG et al. Circular RNA circ-ABCB10 promotes breast cancer proliferation and progression through sponging miR-1271. Am J Cancer Res 2017;7:1566–1576.
Dai X, Kaushik AC, Zhang J. The Emerging Role of Major Regulatory RNAs in Cancer Control. Front Oncol 2019;9:920. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00920.
Tan GZ, Li M, Tan X, et al. MiR-491 suppresses migration and invasion via directly targeting TPX2 in breast cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2019;23:9996–10004. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201911_19566
Wang L, Lv X, Fu X et al. MiR-153 inhibits the resistance of lung cancer to gefitinib via modulating expression of ABCE1. Cancer Biomark 2019;25:361–369. https://doi.org/10.3233/cbm-190094.
Song NS, Pei ZD, Fu G. MiR-1224-5p acts as a tumor suppressor via inhibiting the malignancy of rectal cancer through targeting SLC29A3. IUBMB Life 2020;72:2204–2213. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.2352.
Zhao L, Lou G, Li A et al. lncRNA MALAT1 modulates cancer stem cell properties of liver cancer cells by regulating YAP1 expression via miR-375 sponging. Mol Med Rep 2020;22:1449–1457. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.11196.
Wu Y, Sun X, Song B et al. MiR-375/SLC7A11 axis regulates oral squamous cell carcinoma proliferation and invasion. Cancer Med 2017;6:1686–1697. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1110.
Jin Y, Su Z, Sheng H et al. Circ_0086720 knockdown strengthens the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer via mediating the miR-375/SPIN1 axis. Neoplasma. 2020. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2020_200331N333.
Xi ZW, Xin SY, Zhou LQ et al. Downregulation of rho-associated protein kinase 1 by miR-124 in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2015;21:5454–5464. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5454.
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors made substantial contribution to conception and design, acquisition of the data, or analysis and interpretation of the data; take part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; gave final approval of the revision to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspect of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The present study was approved by the ethical review committee of The First Hospital of Hebei Medical University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wang, H., Li, C. et al. CircTUBGCP3 Contributes to the Malignant Progression of Rectal Cancer. Dig Dis Sci 67, 2957–2970 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-021-07135-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-021-07135-7