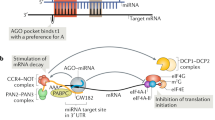
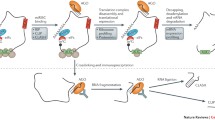
Abstract
The relatively recent discovery of miRNAs has added a completely new dimension to the study of the regulation of gene expression. The mechanism of action of miRNAs, the conservation between diverse species and the fact that each miRNA can regulate a number of targets and phenotypes clearly indicates the importance of these molecules. In this review the current state of knowledge relating to miRNA expression and gene regulation is presented, outlining the key morphological and biochemical features controlled by miRNAs with particular emphasis on the key phenotypes that impact on cell growth in bioreactors, namely proliferation and apoptosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abston LR, Miller WM (2005) Effects of NHE1 expression level on CHO cell responses to environmental stress. Biotechnol Prog 21:562–567
Akao Y, Nakagawa Y, Naoe T (2006) let-7 microRNA functions as a potential growth suppressor in human colon cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull 29:903–906
Al-Fageeh MB, Marchant RJ, Carden MJ, Smales CM (2006) The cold-shock response in cultured mammalian cells: harnessing the response for the improvement of recombinant protein production. Biotechnol Bioeng 93:829–835
Al-Rubeai M, Singh RP (1998) Apoptosis in cell culture. Curr Opin Biotechnol 9:152–156
Ambros V (2003) MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell 113:673–676
Arden N, Betenbaugh MJ (2004) Life and death in mammalian cell culture: strategies for apoptosis inhibition. Trends Biotechnol 22:174–180
Baik JY, Lee MS, An SR, Yoon SK, Joo EJ, Kim YH, Park HW, Lee GM (2006) Initial transcriptome and proteome analyses of low culture temperature-induced expression in CHO cells producing erythropoietin. Biotechnol Bioeng 93:361–371
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bi JX, Shuttleworth J, Al-Rubeai M (2004) Uncoupling of cell growth and proliferation results in enhancement of productivity in p21CIP1-arrested CHO cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 85:741–749
Bohnsack MT, Czaplinski K, Gorlich D (2004) Exportin 5 is a RanGTP-dependent dsRNA-binding protein that mediates nuclear export of pre-miRNAs. RNA 10:185–191
Bracken AP, Ciro M, Cocito A, Helin K (2004) E2F target genes: unraveling the biology. Trends Biochem Sci 29:409–417
Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM (2003) bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell 113:25–36
Brennecke J, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM (2005) Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol 3:e85
Butler M (2005) Animal cell cultures: recent achievements and perspectives in the production of biopharmaceuticals. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68:283–291
Cai X, Hagedorn CH, Cullen BR (2004) Human microRNAs are processed from capped, polyadenylated transcripts that can also function as mRNAs. RNA 10:1957–1966
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, Rassenti L, Kipps T, Negrini M, Bullrich F, Croce CM (2002) Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes mir15 and mir16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:15524–15529
Calin GA, Liu CG, Sevignani C, Ferracin M, Felli N, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Cimmino A, Zupo S, Dono M, Dell’Aquila ML, Alder H, Rassenti L, Kipps TJ, Bullrich F, Negrini M, Croce CM (2004) MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:11755–11760
Carvalhal AV, Marcelino I, Carrondo MJT (2003) Metabolic changes during cell growth inhibition by p27 overexpression. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:164–173
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS (2005) MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 65:6029–6033
Chang S, Johnston RJ Jr, Frokjaer-Jensen C, Lockery S, Hobert O (2004) MicroRNAs act sequentially and asymmetrically to control chemosensory laterality in the nematode. Nature 430:785–789
Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF, Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 303:83–86
Chen JF, Mandel EM, Thomson JM, Wu Q, Callis TE, Hammond SM, Conlon FL, Wang DZ (2006) The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation. Nat Genet 38:228–233
Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J, Ford LP (2005) Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Res 33:1290–1297
Chiang GG, Sisk WP (2005) Bcl-x(L) mediates increased production of humanized monoclonal antibodies in chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 91:779–792
Choi SS, Rhee WJ, Kim EJ, Park TH (2006) Enhancement of recombinant protein production in chinese hamster ovary cells through anti-apoptosis engineering using 30Kc6 gene. Biotechnol Bioeng 95:459–467
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Aqeilan RI, Zupo S, Dono M, Rassenti L, Alder H, Volinia S, Liu CG, Kipps TJ, Negrini M, Croce CM (2005) Mir-15 and mir-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13944–13949
Crea F, Sarti D, Falciani F, Al-Rubeai M (2006) Over-expression of hTERT in CHOK1 results in decreased apoptosis and reduced serum dependency. J Biotechnol 121:109–123
Debbas M, White E (1993) Wild-type p53 mediates apoptosis by E1A, which is inhibited by E1B. Genes Dev 7:546–554
Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, Ketting RF, Hannon GJ (2004) Processing of primary microRNAs by the Microprocessor complex. Nature 432:231–235
Dresios J, Aschrafi A, Owens GC, Vanderklish PW, Edelman GM, Mauro VP (2005) Cold stress-induced protein Rbm3 binds 60S ribosomal subunits, alters microRNA levels, and enhances global protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:1865–1870
Esau C, Kang X, Peralta E, Hanson E, Marcusson EG, Ravichandran LV, Sun Y, Koo S, Perera RJ, Jain R, Dean NM, Freier SM, Bennett CF, Lollo B, Griffey R (2004) MicroRNA-143 regulates adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 279:52361–52365
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs – microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:259–269
Fassnacht D, Rossing S, Singh RP, Al-Rubeai M, Portner R (1999) Influence of bcl-2 on antibody productivity in high cell density perfusion cultures of hybridoma. Cytotechnology 30:95–105
Felli N, Fontana L, Pelosi E, Botta R, Bonci D, Facchiano F, Liuzzi F, Lulli V, Morsilli O, Santoro S, Valtieri M, Calin GA, Liu CG, Sorrentino A, Croce CM, Peschle C (2005) MicroRNAs 221 and 222 inhibit normal erythropoiesis and erythroleukemic cell growth via kit receptor down-modulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:18081–18086
Figueroa B.Jr., Ailor E, Osbourne D, Hardwick JM, Reff M, Betenbaugh MJ (2006) Enhanced cell culture performance using inducible anti-apoptotic genes E1B-19K and Aven in the production of a monoclonal antibody with Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol Bioeng Published online 10 Nov 2006
Fogolin MB, Wagner R, Etcheverrigaray M, Kratje R (2004) Impact of temperature reduction and expression of yeast pyruvate carboxylase on hGM-CSF-producing CHO cells. J Biotechnol 109:179–191
Furukawa K, Ohsuye K (1998) Effect of culture temperature on a recombinant CHO cell line producing a C-terminal α-amidating enzyme. Cytotechnology 26:153–164
Fussenegger M, Bailey JE (1998) Molecular regulation of cell-cycle progression and apoptosis in mammalian cells: implications for biotechnology. Biotech Progress 14:807–833
Fussenegger M, Mazur X, Bailey JE (1997) A novel cytostatic process enhances the productivity of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 55:927–939
Fussenegger M, Schlatter S, Datwyler D, Mazur X, Bailey JE (1998) Controlled proliferation by multigene metabolic engineering enhances the productivity of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Nat Biotechnol 16:468–472
Fussenegger M, Fassnacht D, Schwartz R, Zanghi JA, Graf M, Bailey JE, Portner R (2000) Regulated overexpression of the survival factor bcl-2 in CHO cells increases viable cell density in batch culture and decreases DNA release in extended fixed-bed cultivation. Cytotechnology 32:45–61
Goswami J, Sinskey AJ, Steller H, Stephanopoulos GN, Wang DIC (1999) Apoptosis in batch cultures of Chinese Hamster Ovary cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 62:632–640
Gregory RI, Yan KP, Amuthan G, Chendrimada T, Doratotaj B, Cooch N, Shiekhattar R (2004) The Microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature 432:235–240
Gross A, McDonnell JM, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:1899–1911
Gupta A, Gartner JJ, Sethupathy P, Hatzigeorgiou AG, Fraser NW (2006) Anti-apoptotic function of a microrna encoded by the HSV-1 latency-associated transcript. Nature 442:82–85
Ha I, Wightman B, Ruvkun G (1996) A bulged lin-4/lin-14 RNA duplex is sufficient for Caenorhabditis elegans lin-14 temporal gradient formation. Genes Dev 10:3041–3050
Han J, Lee Y, Yeom KH, Kim YK, Jin H, Kim VN (2004) The Drosha-DGCR8 complex in primary microRNA processing. Genes Dev 18:3016–3027
Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Yamada H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Yatabe Y, Kawahara K, Sekido Y, Takahashi T (2005) A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res 65:9628–9632
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, Powers S, Cordon-Cardo C, Lowe SW, Hannon GJ, Hammond SM (2005) A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 435:828–833
Hutvagner G, Zamore PD (2002) A microRNA in a multiple-turnover RNAi enzyme complex. Science 297:2056–2060
Ifandi V, Al-Rubeai M (2005) Regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis in CHO-K1 cells by the coexpression of c-Myc and Bcl-2. Biotechnol Prog 21:671–677
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M, Menard S, Palazzo JP, Rosenberg A, Musiani P, Volinia S, Nenci I, Calin GA, Querzoli P, Negrini M, Croce CM (2005) Microrna gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 65:7065–7070
Irani N, Beccaria AJ, Wagner R (2002) Expression of recombinant cytoplasmic yeast pyruvate carboxylase for the improvement of the production of human erythropoietin by recombinant BHK-21 cells. J Biotechnol 93:269–282
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom M, Jarvis R, Cheng A, Labourier E, Reinert KL, Brown D, Slack FJ (2005) RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 120:635–647
Katakura Y, Seto P, Miura T, Ohashi H, Teruya K, Shirahata S (1999) Productivity enhancement of recombinant protein in CHO cells via specific promoter activation by oncogenes. Cytotechnology 31:103–109
Kaufmann H, Mazur X, Fussenegger M, Bailey JE (1999) Influence of low temperature on productivity, proteome and protein phosphorylation of CHO cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 63:573–582
Kaufmann H, Mazur X, Marone R, Bailey JE, Fussenegger M (2001) Comparative analysis of two controlled proliferation strategies regarding product quality, influence on tetracycline-regulated gene expression, and productivity. Biotechnol Bioeng 72:592–602
Kim NS, Lee GM (2002) Response of recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cells to hyperosmotic pressure: effect of Bcl-2 overexpression. J Biotechnol 95:237–248
Kim NS, Chang KH, Chung BS, Kim SH, Kim JH, Lee GM (2003) Characterization of humanized antibody produced by apoptosis-resistant CHO cells under sodium butyrate-induced condition. J Microbiol Biotechnol 13:926–936
Krutzfeldt J, Poy MN, Stoffel M (2006) Strategies to determine the biological function of microRNAs. Nat Genet 38 Suppl:S14–S19
Laken HA, Leonard MW (2001) Understanding and modulating apoptosis in industrial cell culture. Curr Opin Biotechnol 12:175–179
Lee SK, Lee GM (2003) Development of apoptosis-resistant dihydrofolate reductase-deficient Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Biotechnol Bioeng 82:872–876
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75:843–854
Lee Y, Jeon K, Lee JT, Kim S, Kim VN (2002) MicroRNA maturation: stepwise processing and subcellular localization. EMBO J 21:4663–4670
Lee Y, Ahn C, Han J, Choi H, Kim J, Yim J, Lee J, Provost P, Radmark O, Kim S, Kim VN (2003) The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature 425:415–419
Lee Y, Kim M, Han J, Yeom KH, Lee S, Baek SH, Kim VN (2004) MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J 23:4051–4060
Lee YS, Kim HK, Chung S, Kim KS, Dutta A (2005) Depletion of human micro-RNA miR-125b reveals that it is critical for the proliferation of differentiated cells but not for the down-regulation of putative targets during differentiation. J Biol Chem 280:16635–16641
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB (2003) Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115:787–798
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20
Lin SY, Johnson SM, Abraham M, Vella MC, Pasquinelli A, Gamberi C, Gottlieb E, Slack FJ (2003) The C elegans hunchback homolog, hbl-1, controls temporal patterning and is a probable microRNA target. Dev Cell 4:639–650
Lowe SW, Ruley HE (1993) Stabilization of the p53 tumor suppressor is induced by adenovirus 5 E1A and accompanies apoptosis. Genes Dev 7:535–545
Lund E, Guttinger S, Calado A, Dahlberg JE, Kutay U (2004) Nuclear export of microRNA precursors. Science 303:95–98
Mastrangelo AJ, Hardwick JM, Bex F, Betenbaugh MJ (2000a) Part I. Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L) limit apoptosis upon infection with alphavirus vectors. Biotechnol Bioeng 67:544–554
Mastrangelo AJ, Hardwick JM, Zou SF, Betenbaugh MJ (2000b) Part II. Overexpression of bcl-2 family members enhances survival of mammalian cells in response to various culture insults. Biotechnol Bioeng 67:555–564
Mazur X, Fussenegger M, Renner WA, Bailey JE (1998) Higher productivity of growth-arrested Chinese hamster ovary cells expressing the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. Biotechnol Prog 14:705–713
Mazur X, Eppenberger HM, Bailey JE, Fussenegger M (1999) A novel autoregulated proliferation-controlled production process using recombinant CHO cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 65:144–150
Meents H, Enenkel B, Eppenberger HM, Werner RG, Fussenegger M (2002) Impact of coexpression and coamplification of sICAM and antiapoptosis determinants bcl-2/bcl-x(L) on productivity, cell survival, and mitochondria number in CHO-DG44 grown in suspension and serum-free media. Biotech Bioeng 80:706–716
Meister G, Landthaler M, Dorsett Y, Tuschl T (2004) Sequence-specific inhibition of microRNA- and siRNA-induced RNA silencing. RNA 10:544–550
Meng F, Henson R, Lang M, Wehbe H, Maheshwari S, Mendell JT, Jiang J, Schmittgen TD, Patel T (2006) Involvement of human micro-RNA in growth and response to chemotherapy in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. Gastroenterology 130:2113–2129
Miura T, Katakura Y, Seto P, Zhang YP, Teruya K, Nishimura E, Kato M, Hashizume S, Shirahata S (2001) Availability of oncogene activated production system for mass production of light chain of human antibody in CHO cells. Cytotechnology 35:9–16
Nairz K, Rottig C, Rintelen F, Zdobnov E, Moser M, Hafen E (2006) Overgrowth caused by misexpression of a microrna with dispensable wild-type function. Dev Biol 291:314–324
Nishimoto S, Nishida E (2006) MAPK signalling: ERK5 versus ERK1/2. EMBO Rep 7:782–786
O’Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT (2005) c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature 435:839–843
Olsen PH, Ambros V (1999) The lin-4 regulatory RNA controls developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans by blocking LIN-14 protein synthesis after the initiation of translation. Dev Biol 216:671–680
Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, Martindale MQ, Kuroda MI, Maller B, Hayward DC, Ball EE, Degnan B, Muller P, Spring J, Srinivasan A, Fishman M, Finnerty J, Corbo J, Levine M, Leahy P, Davidson E, Ruvkun G (2000) Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 408:86–89
Pillai RS, Bhattacharyya SN, Artus CG, Zoller T, Cougot N, Basyuk E, Bertrand E, Filipowicz W (2005) Inhibition of translational initiation by Let-7 MicroRNA in human cells. Science 309:1573–1576
Poy MN, Eliasson L, Krutzfeldt J, Kuwajima S, Ma X, Macdonald PE, Pfeffer S, Tuschl T, Rajewsky N, Rorsman P, Stoffel M (2004) A pancreatic islet-specific microRNA regulates insulin secretion. Nature 432:226–230
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR, Ruvkun G (2000) The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 403:901–906
Roldo C, Missiaglia E, Hagan JP, Falconi M, Capelli P, Bersani S, Calin GA, Volinia S, Liu CG, Scarpa A, Croce CM (2006) Microrna expression abnormalities in pancreatic endocrine and acinar tumors are associated with distinctive pathologic features and clinical behavior. J Clin Oncol 24:4677–4684
Sauerwald TM, Figueroa B, Hardwick JM, Oyler GA, Betenbaugh MJ (2006) Combining caspase and mitochondrial dysfunction inhibitors of apoptosis to limit cell death in mammalian cell cultures. Biotechnol Bioeng 94:362–372
Schuster N, Krieglstein K (2002) Mechanisms of TGF-beta-mediated apoptosis. Cell Tissue Res 307:1–14
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F, Mo YY (2006) Mir-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene Oct 30; [Epub ahead of print]
Simpson NH, Singh RP, Emery AN, Al-Rubeai M (1999) Bcl-2 over-expression reduces growth rate and prolongs G(1) phase in continuous chemostat cultures of hybridoma cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 64:174–186
Slack FJ, Basson M, Liu Z, Ambros V, Horvitz HR, Ruvkun G (2000) The lin-41 RBCC gene acts in the C. elegans heterochronic pathway between the let-7 regulatory RNA and the LIN-29 transcription factor. Mol Cell 5:659–669
Sun XM, Bratton SB, Butterworth M, Macfarlane M, Cohen GM (2002) Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl inhibit CD95-mediated apoptosis by preventing mitochondrial release of Smac/DIABLO and subsequent inactivation of X-linked inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein. J Biol Chem 277:11345–11351
Sung YH, Lee GM (2005) Enhanced human thrombopoietin production by sodium butyrate addition to serum-free suspension culture of Bcl-2-overexpressing CHO cells. Biotechnol Progr 21:50–57
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Osada H, Endoh H, Harano T, Yatabe Y, Nagino M, Nimura Y, Mitsudomi T, Takahashi T (2004) Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res 64:3753–3756
Tanno B, Cesi V, Vitali R, Sesti F, Giuffrida ML, Mancini C, Calabretta B, Raschella G (2005) Silencing of endogenous IGFBP-5 by micro RNA interference affects proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation of neuroblastoma cells. Cell Death Differ 12:213–223
Tey BT, Singh RP, Piredda L, Piacentini M, Al-Rubeai M (2000) Influence of Bcl-2 on cell death during the cultivation of a Chinese hamster ovary cell line expressing a chimeric antibody. Biotechnol Bioeng 68:31–43
Tseng WF, Huang SS, Huang JS (2004) LRP-1/T beta R-V mediates TGF-beta 1-induced growth inhibition in CHO cells. FEBS Lett 562:71–78
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, Prueitt RL, Yanaihara N, Lanza G, Scarpa A, Vecchione A, Negrini M, Harris CC, Croce CM (2006) A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2257–2261
Voorhoeve PM, Le Sage C, Schrier M, Gillis AJ, Stoop H, Nagel R, Liu YP, van Duijse J, Drost J, Griekspoor A, Zlotorynski E, Yabuta N, De Vita G, Nojima H, Looijenga LH, Agami R (2006) A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Cell 124:1169–1181
Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G (1993) Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 75:855–862
Wong DCF, Wong KTK, Nissom PM, Heng CK, Yap MGS (2006) Transcriptional profiling of apoptotic pathways in batch and fed-batch CHO cell cultures. Biotechnol Bioeng 94:373–382
Xu P, Vernooy SY, Guo M, Hay BA (2003) The Drosophila microRNA Mir-14 suppresses cell death and is required for normal fat metabolism. Curr Biol 13:790–795
Yallop C, Svendsen I (2001) The effects of G418 on the growth and metabolism of recombinant mammalian cell lines. Cytotechnology 35:101–114
Yallop C, Nørby PL, Jensen R, Reinbach H, Svendsen I (2003) Characterisation of G418-induced metabolic load in recombinant CHO and BHK cells: effect on the activity and expression of central metabolic enzymes. Cytotechnology 42:87–99
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado AM, Cai J, Peng TI, Jones DP, Wang X (1997) Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science 275:1129–1132
Yekta S, Shih IH, Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNA-directed cleavage of HOXB8 mRNA. Science 304:594–596
Yi R, Qin Y, Macara IG, Cullen BR (2003) Exportin-5 mediates the nuclear export of pre-microRNAs and short hairpin RNAs. Genes Dev 17:3011–3016
Zeng Y, Cullen BR (2004) Structural requirements for pre-microRNA binding and nuclear export by Exportin 5. Nucleic Acids Res 32:4776–4785
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gammell, P. MicroRNAs: recently discovered key regulators of proliferation and apoptosis in animal cells. Cytotechnology 53, 55–63 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-007-9049-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-007-9049-4