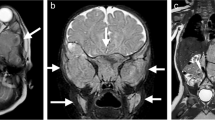
Abstract
Brain metastasis is associated with a particular poor prognosis. Novel insight into the brain metastatic process is therefore warranted. Several preclinical models of brain tumor metastasis have been developed during the last 60 years, and they have in part revealed some of the mechanisms underlying the metastatic process. This review discusses mechanisms of brain metastasis with a key focus of the development of animal model systems. This includes the use of rodent, syngeneic brain metastasis models (spontaneous, chemically induced and genetically engineered models) and human xenotransplantation models (ectopic inoculation and orthotopic models). Current information indicates that none of these fully reflect tumor development seen in patients with metastatic disease. The various model systems used, however, have provided important insight into specific mechanisms of the metastatic process related to the brain. By combining the knowledge obtained from animal models, new important information on the molecular mechanisms behind metastasis will be obtained, leading to the future development of new therapeutic strategies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nathoo N, Chahlavi A, Barnett G, Toms SA (2005) Pathobiology of brain metastases. J Clin Pathol 58:237–242
Palmieri D, Chambers A, Felding-Habermann B, Huang S, Steeg PS (2007) The biology of metastasis to a sanctuary site. Clin Cancer Res 13:1656–1662
Barnholtz-Sloan JS (2004) Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J Clin Oncol 22:2865–2872
Fife KM, Colman MH, Stevens GN, Firth IC, Moon D, Shannon KF, Harman R, Petersen-Schaefer K, Zacest AC, Besser M, Milton GW, McCarthy WH, Thompson JF (2004) Determinants of outcome in melanoma patients with cerebral metastases. J Clin Oncol 22:1293–1300
Steeg P, Camphausen K, Smith Q (2011) Brain metastases as preventive and therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Cancer 11:352–363
Schackert G (2002) Surgery of brain metastases—pro and contra. Onkologie 25:480–481
Tosoni A, Ermani M, Brandes AA (2004) The pathogenesis and treatment of brain metastases: a comprehensive review. Crit Rev Oncol/Hematol 52:199–215
Neves S, Mazal PR, Wanschitz J, Rudnay AC, Drlicek M, Czech T, Wüstinger C, Budka H (2001) Pseudogliomatous growth pattern of anaplastic small cell carcinomas metastatic to the brain. Clin Neuropathol 20:38–42
Gavrilovic IT (2005) Posner JB (2005) Brain metastases: epidemiology and pathophysiology. J Neurooncol 75(1):5–14
Preusser M, Capper D, Ilhan-Mutlu A, Berghoff AS, Birner P, Bartsch R, Marosi C, Zielinski C, Mehta MP, Winkler F, Wick W, von Deimling A (2012) Brain metastases: pathobiology and emerging targeted therapies. Acta Neuropathol 123:205–222
Santarelli J, Sarkissian V, Hou L, Veeravagu A, Tse V (2007) Molecular events of brain metastasis. Neurosurg Focus 22:1–5
Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC (2002) Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer 2:563–572
Eichler AF, Chung E, Kodack DP, Loeffler JS, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2011) The biology of brain metastases—translation to new therapies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8:344–356
Mina LA, Sledge GW (2011) Rethinking the metastatic cascade as a therapeutic target. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8:325–332
Valastyan S, Weinberg RA (2011) Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell 147:275–292
Zhang C, Yu D (2011) Microenvironment determinants of brain metastasis. Cell Biosci 1:8
Cheng X, Hung M-C (2007) Breast cancer brain metastases. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26:635–643
Gavrilovic IT, Posner JB (2005) Brain metastases: epidemiology and pathophysiology. J Neurooncol 75:5–14
Marchetti D, Denkins Y, Reiland J, Greiter-Wilke A, Galjour J, Murry B, Blust J, Roy M (2003) Brain-metastatic melanoma: a neurotrophic perspective. Pathol Oncol Res 9:147–158
Ray PS, Wang J, Qu Y, Sim MS, Shamonki J, Bagaria SP, Ye X, Liu B, Elashoff D, Hoon DS, Walter MA, Martens JW, Richardson AL, Giuliano AE, Cui X (2010) FOXC1 is a potential prognostic biomarker with functional significance in basal-like breast cancer. Cancer Res 70:3870–3876
Paget S (1889) Distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. Lancet 133:571–573
Palmieri D, Bronder JL, Herring JM, Yoneda T, Weil RJ, Stark AM, Kurek R, Vega-Valle E, Feigenbaum L, Halverson D, Vortmeyer AO, Steinberg SM, Aldape K, Steeg PS (2007) Her-2 overexpression increases the metastatic outgrowth of breast cancer cells in the brain. Cancer Res 67:4190–4198
Bendell JC, Domchek SM, Burstein HJ, Harris L, Younger J, Kuter I, Bunnell C, Rue M, Gelman R, Winer E (2003) Central nervous system metastases in women who receive trastuzumab-based therapy for metastatic breast carcinoma. Cancer 97:2972–2977
Clayton AJ, Danson S, Jolly S, Ryder WDJ, Burt PA, Stewart AL, Wilkinson PM, Welch RS, Magee B, Wilson G, Howell A, Wardley AM (2004) Incidence of cerebral metastases in patients treated with trastuzumab for metastatic breast cancer. Br J Cancer 91:639–643
Stemmler HJ, Kahlert S, Siekiera W, Untch M, Heinrich B, Heinemann V (2006) Characteristics of patients with brain metastases receiving trastuzumab for HER2 overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. Breast 15:219–225
Ruan S, Fuller G, Levin V et al (1998) Detection of p21WAF1/Cip1 in brain metastases. J Neurooncol 37(3):223–228
Stark AM, Tongers K, Maass N, Bruner JM, Zhang W (1998) Reduced metastasis-suppressor gene mRNA-expression in breast cancer brain metastases. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 131:191–198
Carvajal RD, Antonescu CR, Wolchok JD, Chapman PB, Roman RA, Teitcher J, Panageas KS, Busam KJ, Chmielowski B, Lutzky J, Pavlick AC, Fusco A, Cane L, Takebe N, Vemula S, Bouvier N, Bastian BC, Schwartz GK (2011) KIT as a therapeutic target in metastatic melanoma. JAMA 305:2327–2334
Korabiowska M, König F, Verheggen R, Schlott T, Cordon-Cardo C, Romeike B, Brinck U (2004) Altered expression and new mutations in DNA mismatch repair genes MLH1 and MSH2 in melanoma brain metastases. Anticancer Res 24:981–986
Palmieri D, Fitzgerald D, Shreeve SM, Hua E, Bronder JL, Weil RJ, Davis S, Stark AM, Merino MJ, Kurek R, Mehdorn HM, Davis G, Steinberg SM, Meltzer PS, Aldape K, Steeg PS (2009) Analyses of resected human brain metastases of breast cancer reveal the association between up-regulation of hexokinase 2 and poor prognosis. Mol Cancer Res 7:1438–1445
Grinberg-Rashi H, Ofek E, Perelman M, Skarda J, Yaron P, Hajduch M, Jacob-Hirsch J, Amariglio N, Krupsky M, Simansky DA, Ram Z, Pfeffer R, Galernter I, Steinberg DM, Ben-Dov I, Rechavi G, Izraeli S (2009) The expression of three genes in primary non-small cell lung cancer is associated with metastatic spread to the brain. Clin Cancer Res 15:1755–1761
Davies MA, Stemke-Hale K, Lin E, Tellez C, Deng W, Gopal YN, Woodman SE, Calderone TC, Ju Z, Lazar AJ, Prieto VG, Aldape K, Mills GB, Gershenwald JE (2009) Integrated molecular and clinical analysis of AKT Activation in metastatic melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 15:7538–7546
Tx Xie (2006) Activation of stat3 in human melanoma promotes brain metastasis. Cancer Res 66:3188–3196
Liu L, Nam S, Tian Y, Yang F, Wu J, Wang Y, Scuto A, Polychronopoulos P, Magiatis P, Skaltsounis L, Jove R (2011) 6-Bromoindirubin-3′-Oxime inhibits JAK/STAT3 signaling and induces apoptosis of human melanoma cells. Cancer Res 71:3972–3979
Kurebayashi J, McLeskey SW, Johnson MD, Lippman ME, Dickson RB, Kern FG (1993) Quantitative demonstration of spontaneous metastasis by MCF-7 human breast cancer cells cotransfected with fibroblast growth factor 4 and LacZ. Cancer Res 53:2178–2187
Bos PD, Zhang XH-F, Nadal C, Shu W, Gomis RR, Nguyen DX, Minn AJ, Vijver MJ, Gerald WL, Foekens JA, Massagué J (2009) Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Nature 459:1005–1009
Küsters B, Leenders WPJ, Wesseling P, Smits D, Verrijp K, Ruiter DJ, Peterw JPW, van der Kogel AJ, de Waal RMW (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor-A(165) induces progression of melanoma brain metastases without induction of sprouting angiogenesis. Cancer Res 62:341–345
Yano S, Shinohara H, Herbst RS, Kuniyasu H, Bucana CD, Ellis LM, Davis DW, McConkey DJ, Fidler IJ (2000) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor is necessary but not sufficient for production and growth of brain metastasis. Cancer Res 60:4959–4967
JuanYin J, Tracy K, Zhang L, Munasinghe J, Shapiro E, Koretsky A, Kelly K (2009) Noninvasive imaging of the functional effects of anti-VEGF therapy on tumor cell extravasation and regional blood volume in an experimental brain metastasis model. Clin Exp Metastasis 26:403–414
Nguyen DX, Chiang AC, Zhang XHF, Kim JY, Kris MG, Ladanyi M, Gerald WL, Massagué J (2009) WNT/TCF signaling through LEF1 and HOXB9 mediates lung adenocarcinoma metastasis. Cell 138:51–62
Nam DH, Jeon HM, Kim S, Kim MH, Lee YJ, Lee MS, Kim H, Joo KM, Lee DS, Price JE, Bang SI, Park WY (2008) Activation of notch signaling in a xenograft model of brain metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 14:4059–4066
Zhang C, Zhang F, Tsan R, Fidler IJ (2009) Transforming growth factor-2 is a molecular determinant for site-specific melanoma metastasis in the brain. Cancer Res 69:828–835
Kato M, Liu W, Yi H, Asai N, Hayakawa A, Kozaki K, Takahashi M, Nakashima I (1998) The herbal medicine Sho-saiko-to inhibits growth and metastasis of malignant melanoma primarily developed in ret-transgenic mice. J Invest Dermatol 111:640–644
MacPherson D, Conkrite K, Tam M, Mukai S, Mu D, Jacks T (2007) Murine bilateral retinoblastoma exhibiting rapid-onset, metastatic progression and N-myc gene amplification. EMBO J 26:784–794
Meuwissen R, Linn SC, Linnoila RI, Zevenhoven J, Mooi WJ, Berns A (2003) Induction of small cell lung cancer by somatic inactivation of both Trp53 and Rb1 in a conditional mouse model. Cancer Cell 4:181–189
Nguyen DX, Massagué J (2007) Genetic determinants of cancer metastasis. Nat Rev Genetics 8:341–352
Nicolson G, Brunson K, Fidler IJ (1978) Specificity of arrest, survival, and growth of selected metastatic variant cell lines. Cancer Res 38:4105–4111
Yoneda T, Williams PJ, Hiraga T, Niewolna M, Nishimura R (2001) A bone-seeking clone exhibits different biological properties from the MDA-MB-231 parental human breast cancer cells and a brain-seeking clone in vivo and in vitro. J Bone Miner Res 16:1486–1495
Weber GF, Ashkar S (2000) Molecular mechanisms of tumor dissemination in primary and metastatic brain cancers. Brain Res Bull 53:421–424
Sagar D, Foss C, Baz R, Pomper MG, Khan ZK, Jain P (2011) Mechanisms of dendritic cell trafficking across the blood–brain barrier. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 7:74–94
Arshad F, Wang L, Sy C, Avraham S, Avraham HK (2011) Blood-brain barrier integrity and breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Pathol Res Int 2011:1–12
Fidler IJ, Yano S, Zhang R, Fujimaki T, Bucana CD (2002) The seed and soil hypothesis: vascularisation and brain metastases. Lancet Oncol 3:53–57
Kienast Y, von Baumgarten L, Fuhrmann M, Klinkert WEF, Goldbrunner R, Herms J, Winkler F (2010) Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis formation. Nat Med 16:116–122
Nguyen D, Bos P, Massagué J (2009) Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat Rev Cancer 9:274–284
Yoshimasu T, Sakurai T, Oura S, Hirai I, Tanino H, Kokawa Y, Naito Y, Okamura Y, Ota I, Tani N, Matsuura N (2004) Increased expression of integrin alpha3beta1 in highly brain metastatic subclone of a human non-small cell lung cancer cell line. Cancer Sci 95:142–148
Hinton CV, Avraham S, Avraham HK (2010) Role of the CXCR4/CXCL12 signaling axis in breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Clin Exp Metastasis 27:97–105
Lee BC, Lee TH, Avraham S, Avraham HK (2004) Involvement of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and its ligand stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha in breast cancer cell migration through human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Mol Cancer Res 2:327–338
Salmaggi A, Maderna E, Calatozzolo C, Gaviani P, Canazza A, Milanesi I, Silvani A, DiMeco F, Carbone A, Pollo B (2009) CXCL12, CXCR4 and CXCR7 expression in brain metastases. Cancer Biol Ther 8:1608–1614
Brunson K, Beattie G, Nicolson G (1978) Selection and altered properties of brain-colonising metastatic melanoma. Nature 272:543–545
Leenders WPJ, Küsters B, Verrijp K, Maass C, Wesseling P, Heerschap A, Ruiter D, Ryan A, de Waal R (2004) Antiangiogenic therapy of cerebral melanoma metastases results in sustained tumor progression via vessel co-option. Clin Cancer Res 10:6222–6230
McGrady B, McCormick D (1992) A murine model of intracranial invasion: morphological observations on central nervous system invasion by murine melanoma cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 10:387–393
Nicolson GL, Kawaguchi T, Kawaguchi M, Van Pelt C (1987) Brain surface invasion and metastasis of murine malignant melanoma variants. J Neurooncol 4:209–218
Carbonell WS, Ansorge O, Sibson N, Muschel R (2009) The vascular basement membrane as “soil” in brain metastasis. PLoS ONE 4:e5857
Fazakas C, Wilhelm I, Nagyőszi P, Farkas AE, Hasko J, Molnar J, Bauer H, Bauer HC, Ayaydin F, Dung NTK, Siklos L, Krizbai IA (2011) Transmigration of melanoma cells through the blood-brain barrier: role of endothelial tight junctions and melanoma-released serine proteases. PLoS ONE 6:e20758
Mendes O, Kim H, Lungu G, Stoica G (2007) MMP2 role in breast cancer brain metastasis development and its regulation by TIMP2 and ERK1/2. Clin Exp Metastasis 24:341–351
Perides G, Zhuge Y, Lin T, Stins MF, Bronson RT, Wu JK (2006) The fibrinolytic system facilitates tumor cell migration across the blood-brain barrier in experimental melanoma brain metastasis. BMC Cancer 6:56
Bugyik E, Dezso K, Reiniger L, László V, Tóvári J, Tímár J, Nagy P, Klepekto W, Döme B, Paku S (2011) Lack of angiogenesis in experimental brain metastases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 70:979–991
Kaplan RN, Rafii S, Lyden D (2006) Preparing the “soil”: the premetastatic niche. Cancer Res 66:11089–11093
Cranmer L, Trevor K, Bandlamuri S, Hersh EM (2005) Rodent models of brain metastasis in melanoma. Melanoma Res 15:325–356
Green E (1968) Handbook on genetically standardized Jax mice. The Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, Maine
Stephenson EM, Stephenson NG (1970) Karyotype analysis of the B16 mouse melanoma with reassessment of the normal mouse idiogram. J Natl Cancer Inst 45:789–800
Fidler IJ (1973) Selection of successive tumour lines for metastasis. Nat New Biol 242:148–149
Schackert G, Fidler IJ (1988) Site-specific metastasis of mouse melanomas and a fibrosarcoma in the brain or meninges of syngeneic animals. Cancer Res 48:3478–3484
Kallman RF, Silini G, Van Putten LM (1967) Factors influencing the quantitative estimation of the in vivo survival of cells from solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 39:539–549
Conley FK (1979) Development of a metastatic brain tumor model in mice. Cancer Res 39:1001–1007
McCutcheon IE, Baranco RA, Katz DA, Saris SC (1990) Adoptive immunotherapy of intracerebral metastases in mice. Journal Neurosurg 72:102–109
Miller FR (1983) Tumor subpopulation interactions in metastasis. Invasion Metastasis 3:234–242
Yamashina K, Heppner GH (2006) Correlation of frequency of induced mutation and metastatic potential in tumor cell lines from a single mouse mammary tumor. Cancer Res 45:4015–4019
Lelekakis M, Moseley JM, Martin TJ, Hards D, Williams E, Ho P, Lowen D, Javni J, Miller FR, Slavin J, Anderson RL (1999) A novel orthotopic model of breast cancer metastasis to bone. Clin Exp Metastasis 17:163–170
Pulaski BA, Ostrand-Rosenberg S (1998) Reduction of established spontaneous mammary carcinoma metastases following immunotherapy with major histocompatibility complex class II and B7.1 cell-based tumor vaccines. Cancer Res 58:1486–1493
Lockman PR, Mittapalli RK, Taskar KS, Rudraraju V, Gril B, Bohn KA, Adkins CE, Roberts A, Thorsheim HR, Gaasch JA, Huang S, Palmieri D, Steeg PS, Smith QR (2010) Heterogeneous Blood-Tumor Barrier Permeability Determines Drug Efficacy in Experimental Brain Metastases of Breast Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16:5664–5678
Kripke ML (1979) Speculations on the role of ultraviolet radiation in the development of malignant melanoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 63:541–548
Fidler IJ, Gruys E, Cifone MA, Barnes Z, Bucana C (1981) Demonstration of multiple phenotypic diversity in a murine melanoma of recent origin. J Natl Cancer Inst 67:947–956
Price JE, Tarin D, Fidler IJ (1988) Influence of organ microenvironment on pigmentation of a metastatic murine melanoma. Cancer Res 48:2258–2264
Radinsky R, Beltran PJ, Tsan R, Zhang R, Cone RD, Fidler IJ (1995) Transcriptional induction of the melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor in brain metastases of murine K-1735 melanoma. Cancer Res 55:141–148
Fujimaki T, Fan D, Staroselsky A, Gohji K, Bucana C, Fidler I (1993) Critical factors regulating site-specific brain metastasis of murine melanomas. Int J Oncol 3:789–799
Schackert G, Simmons RD, Buzbee TM, Huma DA, Fidler IJ (1988) Macrophage infiltration into experimental brain metastases: occurrence through an intact blood-brain barrier. J Natl Cancer Inst 80:1027–1034
Berkelhammer J, Oxenhandler RW, Hook RR, Hennessy JM (1982) Development of a new melanoma model in C57BL/6 mice. Cancer Res 42:3157–3163
Hearing VJ, Cannon GB, Vieira WD, Jiménez-Atiénzar M, Kameyama K, Law LW (1988) JB/MS murine melanoma: a new model for studies on the modulation of differentiation and of tumorigenic and metastatic potential. Int J Cancer 41:275–282
Foureau DM, McKillop IH, Jones CP, Amin A, White RL, Salo JC (2011) Skin tumor responsiveness to interleukin-2 treatment and CD8 Foxp3 + T cell expansion in an immunocompetent mouse model. Cancer Immunol Immunother 60:1347–1356
Kripke ML (1977) Latency, histology, and antigenicity of tumors induced by ultraviolet light in three inbred mouse strains. Cancer Res 37:1395–1400
Raz A, Hanna N, Fidler IJ (1981) In vivo isolation of a metastatic tumor cell variant involving selective and nonadaptive processes. J Natl Cancer Inst 66:183–189
Fidler IJ (2011) The role of the organ microenvironment in brain metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol 21:107–112
Politi K, Pao W (2011) How genetically engineered mouse tumor models provide insights into human cancers. J Clin Oncol 29:2273–2281
Bos PD, Nguyen DX, Massague J (2010) Modeling metastasis in the mouse. Curr Opin Pharmacol 10:571–577
Winter SF, Cooper AB, Greenberg NM (2003) Models of metastatic prostate cancer: a transgenic perspective. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 6:204–211
Schackert G, Fidler IJ (1988) Development of in vivo models for studies of brain metastasis. Int J Cancer 41:589–594
Higuchi M, Robinson DS, Cailleau R, Irie RF, Morton DL (1980) A serologic study of cultured breast cancer cell lines: lack of antibody response to tumour specific membrane antigens in patients. Clin Exp Immunol 39:90–96
Young RK, Cailleau RM, Mackay B, Reeves WJ (1974) Establishment of epithelial cell line MDA-MB-157 from metastatic pleural effusion of human breast carcinoma. In Vitro 9:239–245
Zhang RD, Fidler IJ, Price JE (1991) Relative malignant potential of human breast carcinoma cell lines established from pleural effusions and a brain metastasis. Invasion Metastasis 11:204–215
Lorger M, Felding-Habermann B (2010) Capturing changes in the brain microenvironment during initial steps of breast cancer brain metastasis. Am J Pathol 176:2958–2971
Heyn C, Ronald JA, Ramadan SS, Snir JA, Barry AM, MacKenzie LT, Mikulis DJ, Palmieri D, Bronder JL, Steeg PS, Yoneda T, MacDonald IC, Chambers AF, Rutt BK, Foster PJ (2006) In vivo MRI of cancer cell fate at the single-cell level in a mouse model of breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Magn Reson Med 56:1001–1010
Tester AM, Waltham M, Oh S-J, Bae SN, Bills MM, Walker EC, Kern FG, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Lippman ME, Thompson EW (2004) Pro-matrix metalloproteinase-2 transfection increases orthotopic primary growth and experimental metastasis of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells in nude mice. Cancer Res 64:652–658
Rae JM, Creighton CJ, Meck JM, Haddad BR, Johnson MD (2007) MDA-MB-435 cells are derived from M14 melanoma cells-a loss for breast cancer, but a boon for melanoma research. Breast Cancer Res Treat 104:13–19
Chambers AF (2009) MDA-MB-435 and M14 cell lines: identical but not M14 melanoma? Cancer Res 69:5292–5293
Soule HD, Vazguez J, Long A, Albert S, Brennan M (1973) A human cell line from a pleural effusion derived from a breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 51:1409–1416
Grossi PM, Ochiai H, Archer GE, McLendon RE, Zalutsky MR, Friedman AH, Friedman HS, Bigner DD, Sampson JH (2003) Efficacy of intracerebral microinfusion of trastuzumab in an athymic rat model of intracerebral metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9:5514–5520
Engel LW, Young NA, Tralka TS, Lippman ME, O′Brien SJ, Joyce MJ (1978) Establishment and characterization of three new continuous cell lines derived from human breast carcinomas. Cancer Res 38:3352–3364
Monsky WL, Mouta Carreira C, Tsuzuki Y, Gohongi T, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2002) Role of host microenvironment in angiogenesis and microvascular functions in human breast cancer xenografts: mammary fat pad versus cranial tumors. Clin Cancer Res 8:1008–1013
Price JE (1996) Metastasis from human breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Res Treat 39:93–102
Rye PD, Norum L, Olsen DR, Garman-Vik S, Kaul S, Fodstad O (1996) Brain metastasis model in athymic nude mice using a novel MUC1-secreting human breast-cancer cell line, MA11. Int J Cancer 68:682–687
Lieber M, Smith B, Szakal A, Nelson-Rees W (1976) Todaro G (1976) A continuous tumor-cell line from a human lung carcinoma with properties of type II alveolar epithelial cells. Int J Cancer 17:62–70
Mathieu A, Remmelink M, D’Haene N, Penant S, Gaussin JF, Van Ginckel R, Darro F, Kiss R (2004) Salmon I (2004) Development of a chemoresistant orthotopic human nonsmall cell lung carcinoma model in nude mice: analysis of tumor heterogeneity in relation to the immunohistochemical levels of expression of cyclooxygenase-2, ornithine decarboxylase, lung-related resistance protein, prostaglandin E synthetase, and gluthathione-S-transferase-alpha (GST)-alpha, GST-mu and GST-pi. Cancer 101(8):1908–1918
Sundstrøm T, Daphu I, Wendelbo I, Hodneland E, Lundervold A, Immervoll H, Skaftnesmo KO, Babic M, Jendelova P, Sykova E, Lund-Johansen M, Bjerkvig R, Thorsen F (2013) Automated tracking of nanoparticle labeled melanoma cells improves the predictive power of a brain metastasis model. Cancer Res (in press)
Hart I, Fidler I (1980) Role of organ selectivity in the determination of metastatic patterns of B16 melanoma. Cancer Res 40:2281–2287
Oskarsson T, Acharyya S, Zhang XH, Vanharanta S, Tavazoie SF, Moris PG, Downey RJ, Manova-Todorova K, Brogi E, Massagué J (2011) Breast cancer cells produce tenascin C as a metastatic niche component to colonize the lungs. Nat Med 17:867–874
Wang J, Daphu I, Pedersen PH, Miletic H, Hovland R, Mørk S, Bjerkvig R, Tiron C, McCormack E, Mickelm D, Lorens JB, Immervoll H, Thorsen F (2010) A novel brain metastases model developed in immunodeficient rats closely mimics the growth of metastatic brain tumours in patients. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 37:189–205
Gunasinghe NP, Wells A, Thompson EW, Hugo HJ (2012) Mesenchymal–epithelial transition (MET) as a mechanism for metastatic colonisation in breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 31:469–478
Kraljevic Pavelic S, Sedic M, Bosnjak H, Spaventi S, Pavelic K (2011) Metastasis: new perspectives on an old problem. Mol Cancer 10:22
Fenouille N, Tichet M, Dufies M, Pottier A, Mogha A, Soo JK, Rocchi S, Mallavialle A, Galibert MD, Khammari A, Lacour JP, Ballotti R, Deckert M, Tartare-Deckert S (2012) The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) regulatory factor slug (SNAI2) is a downstream target of sparc and AKT in promoting melanoma cell invasion. PLoS ONE 7:e40378
Ke XS, Li WC, Hovland R, Qu Y, Liu RH, McCormack E, Thorsen F, Olsen JR, Molven A, Kogan-Sakin I, Rotter V, Akslen LA, Oyan AM, Kalland KH (2010) Reprogramming of cell junction modules during stepwise epithelial to mesenchymal transition and accumulation of malignant features in vitro in a prostate cell model. Exp Cell Res 317:234–247
Rahmathulla G, Toms SA, Weil RJ (2012) The molecular biology of brain metastasis. J Oncol 2012:723541
Gjerdrum C, Tiron C, Høiby T, Stefansson I, Haugen H, Sandal T, Collett K, Li S, McCormack E, Gjertsen BT, Micklem DR, Akslen LA, Glackin C, Lorens JB (2010) Axl is an essential epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-induced regulator of breast cancer metastasis and patient survival. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A 107:1124–1129
Bonnomet A, Syne L, Brysse A, Feyereisen E, Thompson EW, Noël A, Birembaut P, Foidart JM, Polette M, Gilles C (2012) A dynamic in vivo model of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions in circulating tumor cells and metastases of breast cancer. Oncogene 31:3741–3753
Cruz-Munoz W, Man S, Xu P, Kerbel RS (2008) Development of a preclinical model of spontaneous human melanoma central nervous system metastasis. Cancer Res 68:4500–4505
Hoffman RM (1999) Orthotopic metastatic mouse models for anticancer drug discovery and evaluation: a bridge to the clinic. Invest New Drugs 17:343–360
Fu XY, Besterman JM, Monosov A, Hoffman RM (1991) Models of human metastatic colon cancer in nude mice orthotopically constructed by using histologically intact patient specimens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:9345–9349
Fu X, Le P, Hoffman RM (1993) A metastatic orthotopic-transplant nude-mouse model of human patient breast cancer. Anticancer Res 13:901–904
Kim MY, Oskarsson T, Acharyya S, Nguyen DX, Zhang XH, Norton L, Massagué J (2009) Tumor self-seeding by circulating cancer cells. Cell 139:1315–1326
Lucignani G, Ottobrini L, Martelli C, Rescigno M, Clerici M (2006) Molecular imaging of cell-mediated cancer immunotherapy. Trends Biotechnol 24:410–418
Lockshin A, Giovanella BC, Stehlin JS (1986) Quantitative evaluation of anticancer agents against human melanoma cells implanted in nude mice. Exp Cell Biol 54:149–154
Price J, Aukerman S, Fidler I (1986) Evidence that the process of murine melanoma metastasis is sequential and selective and contains stochastic elements. Cancer Res 46:5172–5178
Schabet M, Herrlinger U (1998) Animal models of leptomeningeal metastasis. J Neurooncol 38:199–205
Siegal T, Sandbank U, Gabizon A, Siegal T, Mizrachi R, Ben-David E, Catane R (1987) Alteration of blood-brain-CSF barrier in experimental meningeal carcinomatosis. A morphologic and adriamycin-penetration study. J Neurooncol 4:233–242
Hall WA, Myklebust A, Godal A, Nesland JM, Fodstad O (1994) In vivo efficacy of intrathecal transferrin-Pseudomonas exotoxin A immunotoxin against LOX melanoma. Neurosurgery 34:649–655
Poste G (1982) Experimental systems for analysis of the malignant phenotype. Cancer Metastasis Rev 1:141–199
Yi M, Schnitzer J (2009) Impaired tumor growth, metastasis, angiogenesis and wound healing in annexin A1-null mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:17886–17891
Francia G, Cruz-Munoz W, Man S, Xu P, Kerbel RS (2011) Mouse models of advanced spontaneous metastasis for experimental therapeutics. Nat Rev Cancer 11:135–141
Wagner KU (2004) Models of breast cancer: quo vadis, animal modeling? Breast Cancer Res 6:31–38
Hüsemann Y, Klein CA (2009) The analysis of metastasis in transgenic mouse models. Transgenic Res 18:1–5
Klein CA (2003) The systemic progression of human cancer: a focus on the individual disseminated cancer cell–the unit of selection. Adv Cancer Res 89:35–67
Ossowski L, Aguirre-Ghiso JA (2010) Dormancy of metastatic melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 23:41–56
Goss PE, Chambers AF (2010) Does tumour dormancy offer a therapeutic target? Nat Rev Cancer 10:871–877
Townson JL, Chambers AF (2006) Dormancy of solitary metastatic cells. Cell Cycle 5:1744–1750
Naumov GN, MacDonald IC, Weinmeister PM, Kerkvliet N, Nadkarni KV, Wilson SM, Morris VL, Groom AC, Chambers AF (2002) Persistence of solitary mammary carcinoma cells in a secondary site: a possible contributor to dormancy. Cancer Res 62:2162–2168
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Ingvild Wendelbo, Tove Johansen and Bodil Hansen for technical assistance, and Ian Pryme for a critical review of the manuscript. This work was supported by The Norwegian Cancer Society; the Norwegian Research Council; Innovest AS; Strategic Research Programme; Helse-Vest; Haukeland University Hospital; the Bergen Translational Research Program; and Centre de Recherche Public de la Santé, Luxembourg.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daphu, I., Sundstrøm, T., Horn, S. et al. In vivo animal models for studying brain metastasis: value and limitations. Clin Exp Metastasis 30, 695–710 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-013-9566-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-013-9566-9