Summary
Purpose
Matrix metalloproteinases play a crucial role in the cancer invasion and metastasis, angiogenesis and tumorigenicity. A single guanine insertion – the 1G/2G polymorphism in the promoter of the matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP-1) gene creates a binding site for the transcription factor AP-1 and thus may affect the transcription level of MMP-1. The C→T substitution at the polymorphic site of the MMP-9 gene promoter results in a higher transcription activity of the T-allelic promoter trough the loss of binding site for a repressor protein. The aim of this work was to investigate the influence of 1G/2G and C→T polymorphisms on the MMP-1 and MMP-9 level and therefore on the occurrence and progression of breast cancer.
Experimental design
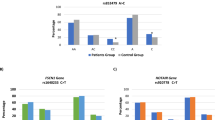
We investigated the distribution of genotypes and frequency of alleles of the 1G/2G and C→T polymorphisms for 270 patients with breast cancer and 300 healthy women served as control. The genotypes were determined by RFLP-PCR. Additionally, we estimated the level of MMP-1 and MMP-9 antigens in tumor samples and normal breast tissue using ELISA.
Results
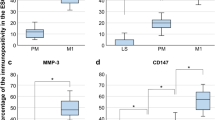
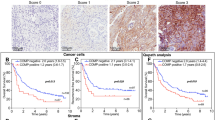
The levels of MMP-1 in tumor samples of node positive patients ware significantly higher than in samples of node negative patients (p<0.05). Increased level of MMP-9 correlates with Bloom-Richardson grading III (p<0.05), increased tumor size (p<0.05) and absence of estrogen and progesterone receptors (p<0.01). Additionally, both MMP-1 and MMP-9 levels were higher in tumor than in the normal breast tissue. We showed the higher risk of metastasis development in lymph node for the 2G/2G genotype (OR=2.14; CI 95% 1.24;3.69) and the 2G allele carriers (OR=1.68; CI 95% 1.19;2.39). We found correlation between the T allele (OR=2.61; CI 95% 1.33;4.87), 2G (OR=2.58; CI 95% 1.35;4.91) and malignance.
Conclusion
The results suggest that MMP-1 is responsible for the local invasion and MMP-9 is associated with the malignance and the growth of the tumor. We suggest that the 2G allele of the 1G/2G MMP-1 gene polymorphism may be associated with the lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer and therefore it can be considered as a progression marker in this disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones JL, Shaw JA, Pringle JH, Walker RA., Priy breast myoepithelial cells exert an invasion-suppressor effect on breast cancer cells via paracrine down-regulation of MMP expression in fibroblasts and tumour cells J Pathol 2003;201:562–572
Curran S, Murray GI., Matrix metalloproteinases in tumour invasion and metastasis J Pathol 1999;189:300–308
Kondo S, Kubota S, Shimo T, Nishida T, Yosimichi G, Eguchi T, Sugahara T, Takigawa M., Connective tissue growth factor increased by hypoxia initiate angiogenesis in collaboration with matrix metalloproteinases Carcinogenesis 2002;23:769–776
Forget MA, Desrosiers RR, Beliveau R, Physiological roles of matrix metalloproteinases: implications for tumor growth and metastasis Can J Physiol Pharmacol 1999;77:465–480
Nikkola J, Vihinen P, Vuoristo MS, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen P, Kahari VM, Pyrhonen S: High serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and matrix metalloproteinase-1 are associated with rapid progression in patients with metastatic melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 11(14): 5158–5166, 2005
Yasui W, Oue N, Aung PP, Matsumura S, Shutoh M, Nakayama H, Molecular-pathological prognostic factors of gastric cancer: a review Gastric Cancer 2005;8(2):86–94
Curran S, Dundas SR, Buxton J, Leeman MF, Ramsay R, Murray GI, Matrix metalloproteinase/tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinase phenotype identifies poor prognosis colorectal cancersClin Cancer Res 2004 10(24):8229–8234
Meller D, Li DQ, Tseng SC, Regulation of collagenase, stromelysin, and gelatinase B in human conctival and conctivochalasis fibroblasts by interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2000 41(10):2922–2929
Bachmeier BE, Nerlich AG, Lichtinghagen R, Sommerhoff CP, Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in breast cancer cell lines of different tumorigenicity Anticancer Res 2001 21:3821–3828
Benaud C, Dickson RB, Thompson EW, Roles of the matrix metalloproteinases in mamy gland development and cancer Breast Cancer Res Treat 1998;50:97–116
Brinckerhoff CE, Rutter JL, Benbow U, Interstitial collagenases as kers of tumor progression Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:4823–30
Jones JL, Walker RA., Control of matrix metalloproteinase activity in cancer J Pathol. 1997;183:377–9
Behrens P, Rothe M, Wellmann A, Krischler J, Wernert N, The Ets-1 transcription factor is up-regulated together with MMP 1 and MMP 9 in the stroma of pre-invasive breast cancer J Pathol 2001 194(1):43–50
Rutter JL, Mitchell TI, Buttice G, Meyers J, Gusella JF, Ozelius LJ, Brinckerhoff CE, A single nucleotide polymorphism in the matrix metalloproteinase-1 promoter creates an Ets binding site and augments transcription Cancer Res 1998 58(23):5321–5325
Jurajda M, Muzik J, Izakovicova Holla L, Vacha J, A newly identified single nucleotide polymorphism in the promoter of the matrix metalloproteinase-1 gene Mol Cell Prob 16:63–66, 2002
Kanamori Y, Matsushima M, Minaguchi T, Kobayashi K, Sagae S, Kudo R, Terakawa N, Nakamura Y: Correlation between expression of the matrix metalloproteinase-1 gene in ovarian cancers and an insertion/deletion polymorphism in its promoter region. Cancer Res 59(17): 4225–4227, 1999
Nishioka Y, Kobayashi K, Sagae S, Ishioka S, Nishikawa A, Matsushima M, Kanamori Y, Minaguchi T, Nakamura Y, Tokino T, Kudo R, A single nucleotide polymorphism in the matrix metalloproteinase-1 promoter in endometrial carcinomas Jpn J Cancer Res 2000;91:612–615
Zhang B, Ye S, Herrmann SM, Eriksson P, de Maat M, Evans A, Arveiler D, Luc G, Cambien F, Hamsten A, Watkins H, Henney AM, Functional polymorphism in the regulatory region of gelatinase B gene in relation to severity of coronary atherosclerosis Circulation 1999;99:1788–1794
Dunleavey L, Beyzade S, Ye S, Rapid genotype analysis of the matrix metalloproteinase-1 gene 1G/2G polymorphism that is associated with risk of cancer Matrix Biol 2000;19:175–177
Weiss L, Comments on hematogenous metastatic patterns in humans as revealed by autopsy Clin Exp Metastasis. 1992 10:191–199
Iwata H., Kobayashi S., Iwase H., Masaoka A., Fujimoto N., Okada Y, Production of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in human breast carcinomas Jpn J Cancer Res 1999;87:602–611
Itoh F., Yamamoto H., Hinoda Y., Imai K, Enhanced secretion and activation of ,matrylisin during malignant conversion of human colorectal epithelium and its relationship with invasive potential of colon cancer cells Cancer (Phila.) 1996;77:1717–1721
Benbow U, Schoenermark MP, Orndorff KA, Givan AL, Brinckerhoff CE, :Human breast cancer cells activate procollagenase-1 and invade type I collagen: invasion is inhibited by all-trans retinoic acid Clin Exp Metastasis 17: 231–238, 1999
Balduyck M, Zerimech F, Gouyer V, Lemaire R, Hemon B, Grard G, Thiebaut C, Lemaire V, Dacquembronne E, Duhem T, Lebrun A, Dejonghe MJ, Huet G, Specific expression of matrix metalloproteinases 1, 3, 9 and 13 associated with invasiveness of breast cancer cells in vitro Clin Exp Metastasis 18:171–178, 2000
Biondi ML, Turri O, Leviti S, Seminati R, Cecchini F, Bernini M, Ghilardi G, Guagnellini E: MMP1 and MMP3 polymorphisms in promoter regions and cancer. Clin Chem. 46 (12): 2023–2024, 2000
Ghilardi G, Biondi ML, Caputo M, Leviti S, DeMonti M, Guagnellini E, Scorza R: A single nucleotide polymorphism in the matrix metalloproteinase-3 promoter enhances breast cancer susceptibility Clin Cancer Res 8(12): 3820–3823, 2002
Tower GB, Coon CI, Brinckerhoff CE, The 2G single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the MMP-1 promoter contributes to high levels of MMP-1 transcription in MCF-7/ADR breast cancer cells Breast Cancer Res Treat 2003;82:75–82
van der Stappen JW, Hendriks T, Wobbes T., Correlation between collagenolytic activity and grade of histological differentiation in colorectal tumors Int J Cancer 1990;45:1071–1078
Li HC, Cao DC, Liu Y, Hou YF, Wu J, Lu JS, Di GH, Liu G, Li FM, Ou ZL, Jie C, Shen ZZ, Shao ZM: Prognostic value of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) in patients with lymph node-negative breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat 88(1): 75–85, 2004
Ghilardi G, Biondi ML, Mangoni J, Leviti S, DeMonti M, Guagnellini E, Scorza R, Matrix metalloproteinase-1 promoter polymorphism 1G/2G is correlated with colorectal cancer invasiveness Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:2344–2346
Goto F, Goto K, Weindel K, Folkman Synergistic effects of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor on the proliferation and cord formation of bovine capillary endothelial. cells within collagen gels J Lab Invest 1993;69:508–517
Chantrain CF, Shimada H, Jodele S, Groshen S, Ye W, Shalinsky DR, Werb Z, Coussens LM, lerck YA., Stromal matrix metalloproteinase-9 regulates the vascular architecture in neuroblastoma by promoting pericyte recruitment Cancer Res. 2004; 64:1675–1686
Lee PP, Hwang JJ, Murphy G, Ip MM., Functional significance of MMP-9 in tumor necrosis factor-induced proliferation and branching morphogenesis of mamy epithelial cells Endocrinology. 2000;141:3764–3773
Duffy MJ, Blaser J, Duggan C, McDermott E, O’Higgins N, Fennelly JJ, Tschesche H., Assay of matrix metalloproteases types 8 and 9 by ELISA in human breast cancer Br J Cancer. 1995;71:1025–1028
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the grants 6P05A 045 21 from KBN (KP) and 505/363 from University of Lodz (JB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Address for offprints and correspondence: Janusz Blasiak, Department of Molecular Genetics, University of Lodz, Banacha 12/16, 90-237 Lodz, Poland; Tel.: +48-42-635-44-89; Fax: +48-42-635-44-84; E-mail: januszb@biol.uni.lodz.pl
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Przybylowska, K., Kluczna, A., Zadrozny, M. et al. Polymorphisms of the promoter regions of matrix metalloproteinases genes MMP-1 and MMP-9 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 95, 65–72 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-9042-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-9042-6