Abstract.
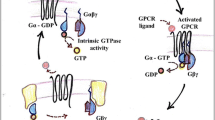
Heterotrimeric G-proteins are intracellular partners of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). GPCRs act on inactive Gα·GDP/Gβγ heterotrimers to promote GDP release and GTP binding, resulting in liberation of Gα from Gβγ. Gα·GTP and Gβγ target effectors including adenylyl cyclases, phospholipases and ion channels. Signaling is terminated by intrinsic GTPase activity of Gα and heterotrimer reformation — a cycle accelerated by ‘regulators of G-protein signaling’ (RGS proteins). Recent studies have identified several unconventional G-protein signaling pathways that diverge from this standard model. Whereas phospholipase C (PLC) β is activated by Gαq and Gβγ, novel PLC isoforms are regulated by both heterotrimeric and Ras-superfamily G-proteins. An Arabidopsis protein has been discovered containing both GPCR and RGS domains within the same protein. Most surprisingly, a receptor-independent Gα nucleotide cycle that regulates cell division has been delineated in both Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster. Here, we revisit classical heterotrimeric G-protein signaling and explore these new, non-canonical G-protein signaling pathways.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Evanko D. S., Thiyagarajan M. M., Siderovski D. P. and Wedegaertner P. B. (2001) Gbeta gamma isoforms selectively rescue plasma membrane localization and palmitoylation of mutant Galphas and Galphaq. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 23945–23953
Chen C. A. and Manning D. R. (2001) Regulation of G proteins by covalent modification. Oncogene 20: 1643–1652
Robillard L., Ethier N., Lachance M. and Hebert T. E. (2000) Gbetagamma subunit combinations differentially modulate receptor and effector coupling in vivo. Cell Signal. 12: 673–682
Brandt D. R. and Ross E. M. (1985) GTPase activity of the stimulatory GTP-binding regulatory protein of adenylate cyclase, Gs. Accumulation and turnover of enzyme-nucleotide intermediates. J. Biol. Chem. 260: 266–272
Higashijima T., Ferguson K. M., Sternweis P. C., Smigel M. D. and Gilman A. G. (1987) Effects of Mg2+ and the beta gamma-subunit complex on the interactions of guanine nucleotides with G proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 262: 762–766
Wall M. A., Posner B. A. and Sprang S. R. (1998) Structural basis of activity and subunit recognition in G protein heterotrimers. Structure 6: 1169–1183
Ford C. E., Skiba N. P., Bae H., Daaka Y., Reuveny E., Shekter L. R. et al. (1998) Molecular basis for interactions of G protein betagamma subunits with effectors. Science 280: 1271–1274
Li Y., Sternweis P. M., Charnecki S., Smith T. F., Gilman A. G., Neer E. J. et al. (1998) Sites for Galpha binding on the G protein beta subunit overlap with sites for regulation of phospholipase Cbeta and adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem 273: 16265–16272
Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P. and Gautam N. (1991) Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science 252: 802–808
Nurnberg B., Gudermann T. and Schultz G. (1995) Receptors and G proteins as primary components of transmembrane signal transduction. Part 2. G proteins: structure and function. J. Mol. Med. 73: 123–132
Wedegaertner P. B., Wilson P. T. and Bourne H. R. (1995) Lipid modifications of trimeric G proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 503–506
Peitzsch R. M. and McLaughlin S. (1993) Binding of acylated peptides and fatty acids to phospholipid vesicles: pertinence to myristoylated proteins. Biochemistry 32: 10436–10443
Grassie M. A., McCallum J. F., Guzzi F., Magee A. I., Milligan G. and Parenti M. (1994) The palmitoylation status of the G-protein G(o)1 alpha regulates its activity of interaction with the plasma membrane. Biochem. J. 302: 913–920
Galbiati F., Guzzi F., Magee A. I., Milligan G. and Parenti M. (1994) N-terminal fatty acylation of the alpha-subunit of the G-protein Gi1: only the myristoylated protein is a substrate for palmitoylation. Biochem. J. 303: 697–700
Mumby S. M., Kleuss C. and Gilman A. G. (1994) Receptor regulation of G-protein palmitoylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 2800–2804
Kisselev O., Ermolaeva M. and Gautam N. (1995) Efficient interaction with a receptor requires a specific type of prenyl group on the G protein gamma subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 25356–25358
Moffett S., Brown D. A. and Linder M. E. (2000) Lipid-dependent targeting of G proteins into rafts. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 2191–2198
Myung C. S., Yasuda H., Liu W. W., Harden T. K. and Garrison J. C. (1999) Role of isoprenoid lipids on the heterotrimeric G protein gamma subunit in determining effector activation. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 16595–16603
Dohlman H. G., Song J., Ma D., Courchesne W. E. and Thorner J. (1996) Sst2, a negative regulator of pheromone signaling in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae: expression, localization and genetic interaction and physical association with Gpa1 (the G-protein alpha subunit). Mol. Cell. Biol. 16: 5194–5209
Fletcher J. E., Lindorfer M. A., DeFilippo J. M., Yasuda H., Guilmard M. and Garrison J. C. (1998) The G protein beta5 subunit interacts selectively with the Gq alpha subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 636–644
Clapham D. E. and Neer E. J. (1997) G protein beta gamma subunits. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 37: 167–203
Huang L., Shanker Y. G., Dubauskaite J., Zheng J. Z., Yan W., Rosenzweig S. et al. (1999) Ggamma13 colocalizes with gustducin in taste receptor cells and mediates IP3 responses to bitter denatonium. Nat. Neurosci. 2: 1055–1062
Ray K., Kunsch C., Bonner L. M. and Robishaw J. D. (1995) Isolation of cDNA clones encoding eight different human G protein gamma subunits, including three novel forms designated the gamma 4, gamma 10, and gamma 11 subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 21765–21771
Jones M. B., Siderovski D. P. and Hooks S. B. (2004) The Gbg dimer as a novel source of selectivity in G-protein signaling: GGL-ing at convention. Mol. Interv. 4: 200–214
Schmidt C. J., Thomas T. C., Levine M. A. and Neer E. J. (1992) Specificity of G protein beta and gamma subunit interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 13807–13810
Muller S., Straub A., Schroder S., Bauer P. H. and Lohse M. J. (1996) Interactions of phosducin with defined G protein beta gamma-subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 11781–11786
Wolfe J. T., Wang H., Howard J., Garrison J. C. and Barrett P. Q. (2003) T-type calcium channel regulation by specific G-protein betagamma subunits. Nature 424: 209–213
Kleuss C., Scherubl H., Hescheler J., Schultz G. and Wittig B. (1993) Selectivity in signal transduction determined by gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. Science 259: 832–834
Wang Q., Mullah B., Hansen C., Asundi J. and Robishaw J. D. (1997) Ribozyme-mediated suppression of the G protein gamma7 subunit suggests a role in hormone regulation of adenylylcyclase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 26040–26048
Wang Q., Mullah B. K. and Robishaw J. D. (1999) Ribozyme approach identifies a functional association between the G protein beta1gamma7 subunits in the beta-adrenergic receptor signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 17365–17371
Schwindinger W. F., Betz K. S., Giger K. E., Sabol A., Bronson S. K. and Robishaw J. D. (2003) Loss of G protein gamma 7 alters behavior and reduces striatal alpha(olf) level and cAMP production. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 6575–6579
Wang Q., Jolly J. P., Surmeier J. D., Mullah B. M., Lidow M. S., Bergson C. M. et al. (2001) Differential dependence of the D1 and D5 dopamine receptors on the G protein gamma 7 subunit for activation of adenylylcyclase. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 39386–39393
Sprang S. R. (1997) G protein mechanisms: insights from structural analysis. Annu. Rev. of Biochem. 66: 639–678
Sondek J., Lambright D. G., Noel J. P., Hamm H. E. and Sigler P. B. (1994) GTPase mechanism of Gproteins from the 1.7-A crystal structure of transducin alpha-GDP-AIF-4. Nature 372: 276–279
Lambright D. G., Noel J. P., Hamm H. E. and Sigler P. B. (1994) Structural determinants for activation of the alpha-subunit of a heterotrimeric G protein. Nature 369: 621–628
Lambright D. G., Sondek J., Bohm A., Skiba N. P., Hamm H. E. and Sigler P. B. (1996) The 2.0 A crystal structure of a heterotrimeric G protein. Nature 379: 311–319
Tesmer J. J., Berman D. M., Gilman A. G. and Sprang S. R. (1997) Structure of RGS4 bound to AlF4-activated G(i alpha1): stabilization of the transition state for GTP hydrolysis. Cell 89: 251–261
Coleman D. E., Berghuis A. M., Lee E., Linder M. E., Gilman A. G. and Sprang S. R. (1994) Structures of active conformations of Gi alpha 1 and the mechanism of GTP hydrolysis. Science 265: 1405–1412
Sternweis P. C. and Gilman A. G. (1982) Aluminum: a requirement for activation of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by fluoride. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79: 4888–4891
Apanovitch D. M., Slep K. C., Sigler P. B. and Dohlman H. G. (1998) Sst2 is a GTPase-activating protein for Gpa1: purification and characterization of a cognate RGS-Galpha protein pair in yeast. Biochemistry 37: 4815–4822
Berman D. M., Kozasa T. and Gilman A. G. (1996) The GTPase-activating protein RGS4 stabilizes the transition state for nucleotide hydrolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 27209–27212
Graziano M. P. and Gilman A. G. (1989) Synthesis in Escherichia coli of GTPase-deficient mutants of Gs alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 264: 15475–15482
Traut T. W. (1994) The functions and consensus motifs of nine types of peptide segments that form different types of nucleotide-binding sites. Eur. J. Biochem. 222: 9–19
Nassar N., Horn G., Herrmann C., Scherer A., McCormick F. and Wittinghofer A. (1995) The 2.2 A crystal structure of the Ras-binding domain of the serine/threonine kinase c-Raf1 in complex with Rap1A and a GTP analogue. Nature 375}: 554–560
Polekhina G., Thirup S., Kjeldgaard M., Nissen P., Lippmann C. and Nyborg J. (1996) Helix unwinding in the effector region of elongation factor EF-Tu-GDP. Structure 4: 1141–1151
Tong L. A., de Vos A. M., Milburn M. V. and Kim S. H. (1991) Crystal structures at 2.2 A resolution of the catalytic domains of normal ras protein and an oncogenic mutant complexed with GDP. J. Mol. Biol. 217: 503–516
Grishina G. and Berlot C. H. (1998) Mutations at the domain interface of GSalpha impair receptor-mediated activation by altering receptor and guanine nucleotide binding. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 15053–15060
Noel J. P., Hamm H. E. and Sigler P. B. (1993) The 2.2 A crystal structure of transducin-alpha complexed with GTP gamma S. Nature 366: 654–663
Wall M. A., Coleman D. E., Lee E., Iniguez-Lluhi J. A., Posner B. A., Gilman A. G. et al. (1995) The structure of the G protein heterotrimer Gialpha1beta1gamma2. Cell 83: 1047–1058
Preininger A. M., Van Eps N., Yu N. J., Medkova M., Hubbell W. L. and Hamm H. E. (2003) The myristoylated amino terminus of Galpha(i)(1) plays a critical role in the structure and function of Galpha(i)(1) subunits in solution. Biochemistry 42: 7931–7941
Neer E. J., Schmidt C. J., Nambudripad R. and Smith T. F. (1994) The ancient regulatory-protein family of WD-repeat proteins. Nature 371: 297–300
Sondek J., Bohm A., Lambright D. G., Hamm H. E. and Sigler P. B. (1996) Crystal structure of a G-protein beta gamma dimer at 2.1A resolution. Nature 379: 369–374
Yan K. and Gautam N. (1996) A domain on the G protein beta subunit interacts with both adenylyl cyclase 2 and the muscarinic atrial potassium channel. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 17597–17600
Leberer E., Dignard D., Hougan L., Thomas D. Y. and Whiteway M. (1992) Dominant-negative mutants of a yeast G-protein beta subunit identify two functional regions involved in pheromone signalling. EMBO J. 11: 4805–4813
Sutherland E. W. and Rall T. W. (1958) Fractionation and characterization of a cyclic adenine ribonucleotide formed by tissue particles. J. Biol. Chem. 232: 1077–1091
Rall T. W., Sutherland E. W. and Berthet J. (1957) The relationship of epinephrine and glucagon to liver phosphorylase IV Effect of epinephrine and glucagon on the reactivation of phosphorylase in liver homogenates. J. Biol. Chem. 224: 463–475
Ross E. M. and Gilman A. G. (1977) Resolution of some components of adenylate cyclase necessary for catalytic activity. J. Biol. Chem. 252: 6966–6969
Smith S. K. and Limbird L. E. (1982) Evidence that human platelet alpha-adrenergic receptors coupled to inhibition of adenylate cyclase are not associated with the subunit of adenylate cyclase ADP-ribosylated by cholera toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 257: 10471–10478
Hsia J. A., Moss J., Hewlett E. L. and Vaughan M. (1984) ADP-ribosylation of adenylate cyclase by pertussis toxin. Effects on inhibitory agonist binding. J. Biol. Chem. 259: 1086–1090
Hildebrandt J. D. and Birnbaumer L. (1983) Inhibitory regulation of adenylyl cyclase in the absence of stimulatory regulation. Requirements and kinetics of guanine nucleotide-induced inhibition of the cyc-S49 adenylyl cyclase. J. Biol. Chem. 258: 13141–13147
Hildebrandt J. D., Sekura R. D., Codina J., Iyengar R., Manclark C. R. and Birnbaumer L. (1983) Stimulation and inhibition of adenylyl cyclases mediated by distinct regulatory proteins. Nature 302: 706–709
Sunahara R. K. and Taussig R. (2002) Isoforms of mammalian adenylyl cyclase: multiplicities of signaling. Mol. Interv. 2: 168–184
Hanoune J. and Defer N. (2001) Regulation and role of adenylyl cyclase isoforms. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 41: 145–174
Buck L. B. (2000) The molecular architecture of odor and pheromone sensing in mammals. Cell 100: 611–618
Margolskee R. F. (2002) Molecular mechanisms of bitter and sweet taste transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 1–4
Arshavsky V. Y., Lamb T. D. and Pugh E. N. Jr (2002) G proteins and phototransduction. Annu. Rev. Physio.l 64: 153–187
Rhee S. G. (2001) Regulation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 70: 281–312
Worthylake D. K., Rossman K. L. and Sondek J. (2000) Crystal structure of Rac1 in complex with the guanine nucleotide exchange region of Tiam1. Nature 408: 682–688
Longenecker K. L., Lewis M. E., Chikumi H., Gutkind J. S. and Derewenda Z. S. (2001) Structure of the RGS-like do-main from PDZ-RhoGEF: linking heterotrimeric G protein-coupled signaling to Rho GTPases. Structure 9: 559–569
Fukuhara S., Murga C., Zohar M., Igishi T. and Gutkind J. S. (1999) A novel PDZ domain containing guanine nucleotide exchange factor links heterotrimeric G proteins to Rho. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 5868–5879
Booden M. A., Siderovski D. P. and Der C. J. (2002) Leukemia-associated Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor promotes G alpha q-coupled activation of RhoA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22: 4053–4061
Vogt S., Grosse R., Schultz G. and Offermanns S. (2003) Receptor-dependent RhoA activation in G12/G13-deficient cells: genetic evidence for an involvement of Gq/G11. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 28743–28749
Kozasa T., Jiang X., Hart M. J., Sternweis P. M., Singer W. D., Gilman A. G. et al. (1998) p115 RhoGEF, a GTPase activating protein for Galpha12 and Galpha13. Science 280: 2109–2111
Hart M. J., Jiang X., Kozasa T., Roscoe W., Singer W. D., Gilman A. G. et al. (1998) Direct stimulation of the guanine nucleotide exchange activity of p115 RhoGEF by Galpha13. Science 280: 2112–2114
Zohn I. E., Klinger M., Karp X., Kirk H., Symons M., Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M. et al. (2000) G2A is an oncogenic G protein-coupled receptor. Oncogene 19: 3866–3877
Whitehead I. P., Zohn I. E. and Der C. J. (2001) Rho GTPase-dependent transformation by G protein coupled receptors. Oncogene 20: 1547–1555
Martin C. B., Mahon G. M., Klinger M. B., Kay R. J., Symons M., Der C. J. et al. (2001) The thrombin receptor, PAR-1, causes transformation by activation of Rho-mediated signaling pathways. Oncogene 20: 1953–1963
Fukuhara S., Chikumi H. and Gutkind J. S. (2001) RGS-containing RhoGEFs: the missing link between transforming G proteins and Rho? Oncogene 20: 1661–1668
Logothetis D. E., Kurachi Y., Galper J., Neer E. J. and Clapham D. E. (1987) The beta gamma subunits of GTPbinding proteins activate the muscarinic K+ channel in heart. Nature 325: 321–326
Lei Q., Jones M. B., Talley E. M., Schrier A. D., McIntire W. E., Garrison J. C. et al. (2000) Activation and inhibition of G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium (Kir3) channels by G protein beta gamma subunits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 9771–9776
Huang C. L., Slesinger P. A., Casey P. J., Jan Y. N. and Jan L. Y. (1995) Evidence that direct binding of G beta gamma to the GIRK1 G protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ channel is important for channel activation. Neuron 15: 1133–1143
Huang C. L., Jan Y. N. and Jan L. Y. (1997) Binding of the G protein betagamma subunit to multiple regions of G proteingated inward-rectifying K+ channels. FEBS Lett. 405: 291–298
Inanobe A., Morishige K. I., Takahashi N., Ito H., Yamada M., Takumi T. et al. (1995) G beta gamma directly binds to the carboxyl terminus of the G protein-gated muscarinic K+ channel, GIRK1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 212: 1022–1028
Kunkel M. T. and Peralta E. G. (1995) Identification of domains conferring G protein regulation on inward rectifier potassium channels. Cell 83: 443–449
Doupnik C. A., Dessauer C. W., Slepak V. Z., Gilman A. G., Davidson N. and Lester H. A. (1996) Time resolved kinetics of direct G beta 1 gamma 2 interactions with the carboxyl terminus of Kir3.4 inward rectifier K+ channel subunits. Neuropharmacology 35: 923–931
Dascal N. (1997) Signalling via the G protein-activated K+ channels. Cell Signal. 9: 551–573
Mark M. D. and Herlitze S. (2000) G-protein mediated gating of inward-rectifier K+ channels. Eur. J. Biochem. 267: 5830–5836
Kammermeier P. J., Ruiz-Velasco V. and Ikeda S. R. (2000) A voltage-independent calcium current inhibitory pathway activated by muscarinic agonists in rat sympathetic neurons requires both Galpha q/11 and Gbeta gamma. J. Neurosci. 20: 5623–5629
Delmas P., Abogadie F. C., Buckley N. J. and Brown D. A. (2000) Calcium channel gating and modulation by transmitters depend on cellular compartmentalization. Nat. Neurosci. 3: 670–678
Lu Q., AtKisson M. S., Jarvis S. E., Feng Z. P., Zamponi G. W. and Dunlap K. (2001) Syntaxin 1A supports voltage-dependent inhibition of alpha1B Ca2+ channels by Gbetagamma in chick sensory neurons. J. Neurosci. 21: 2949–2957
Garcia D. E., Li B., Garcia-Ferreiro R. E., Hernandez-Ochoa E. O., Yan K., Gautam N. et al. (1998) G-protein beta-subunit specificity in the fast membrane-delimited inhibition of Ca2+ channels. J. Neurosci. 18: 9163–9170
Furukawa T., Miura R., Mori Y., Strobeck M., Suzuki K., Ogihara Y. et al. (1998) Differential interactions of the C terminus and the cytoplasmic I–II loop of neuronal Ca2+ channels with G-protein alpha and beta gamma subunits. II. Evidence for direct binding. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 17595–17603
Mirshahi T., Mittal V., Zhang H., Linder M. E. and Logothetis D. E. (2002) Distinct sites on G protein beta gamma subunits regulate different effector functions. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 36345–36350
Yamauchi J., Nagao M., Kaziro Y. and Itoh H. (1997) Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase by signaling through G protein-coupled receptors. Involvement of Gbetagamma and Galphaq/11 subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 27771–27777
Coso O. A., Teramoto H., Simonds W. F. and Gutkind J. S. (1996) Signaling from G protein-coupled receptors to c-Jun kinase involves beta gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins acting on a Ras and Rac1-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 3963–3966
Crespo P., Xu N., Simonds W. F. and Gutkind J. S. (1994) Ras-dependent activation of MAP kinase pathway mediated by G-protein beta/gamma subunits. Nature 369: 418–420
Faure M., Voyno-Yasenetskaya T. A. and Bourne H. R. (1994) cAMP and beta/gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins stimulate the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in COS-7 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 7851–7854
Stephens L. R., Eguinoa A., Erdjument-Bromage H., Lui M., Cooke F., Coadwell J. et al. (1997) The G beta gamma sensitivity of a PI3K is dependent upon a tightly associated adaptor, p101. Cell 89: 105–114
Maier U., Babich A. and Nurnberg B. (1999) Roles of noncatalytic subunits in gbetagamma-induced activation of class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase isoforms beta and gamma. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 29311–29317
Maier U., Babich A., Macrez N., Leopoldt D., Gierschik P., Illenberger D. et al. (2000) Gbeta 5gamma 2 is a highly selective activator of phospholipid-dependent enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 13746–13754
Stephens L., Smrcka A., Cooke F. T., Jackson T. R., Sternweis P. C. and Hawkins P. T. (1994) A novel phosphoinositide 3 kinase activity in myeloid-derived cells is activated by G protein beta gamma subunits. Cell 77: 83–93
Gao B. N. and Gilman A. G. (1991) Cloning and expression of a widely distributed (type IV) adenylyl cyclase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 10178–10182
Tang W. J. and Gilman A. G. (1991) Type-specific regulation of adenylyl cyclase by G protein beta gamma subunits. Science 254: 1500–1503
Taussig R., Tang W. J., Hepler J. R. and Gilman A. G. (1994) Distinct patterns of bidirectional regulation of mammalian adenylyl cyclases. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 6093–6100
Boyer J. L., Waldo G. L. and Harden T. K. (1992) Beta gamma-subunit activation of G-protein-regulated phospholipase C. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 25451–25456
Wing M. R., Houston D., Kelley G. G., Der C. J., Siderovski D. P. and Harden T. K. (2001) Activation of phospholipase C-epsilon by heterotrimeric G protein betagamma-subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 48257–48261
Haga T., Haga K. and Kameyama K. (1994) G protein-coupled receptor kinases. J. Neurochem. 63: 400–412
Pitcher J. A., Freedman N. J. and Lefkowitz R. J. (1998) G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67: 653–692
Welch H. C., Coadwell W. J., Ellson C. D., Ferguson G. J., Andrews S. R., Erdjument-Bromage H. et al. (2002) P-Rex1, a PtdIns(3,4,5)P3- and Gbetagamma-regulated guanine-nucleotide exchange factor for Rac. Cell 108: 809–821
Lodowski D. T., Pitcher J. A., Capel W. D., Lefkowitz R. J. and Tesmer J. J. (2003) Keeping G proteins at bay: a complex between G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 and Gbetagamma. Science 300}: 1256–1262
Berstein G., Blank J. L., Jhon D. Y., Exton J. H., Rhee S. G. and Ross E. M. (1992) Phospholipase C-beta 1 is a GTPase-activating protein for Gq/11, its physiologic regulator. Cell 70: 411–418
Siderovski D. P., Hessel A., Chung S., and Tyers M. (1996) A new family of regulators of G-protein-coupled receptors? Curr. Biol.} 6: 211–212
Koelle M. R. and Horvitz H. R. (1996) EGL-10 regulates G protein signaling in the C. elegans nervous system and shares a conserved domain with many mammalian proteins. Cell 84: 115–125
Druey K. M., Blumer K. J., Kang V. H. and Kehrl J. H. (1996) Inhibition of G-protein-mediated MAP kinase activation by a new mammalian gene family. Nature 379: 742–746
Neubig R. R. and Siderovski D. P. (2002) Regulators of G-protein signalling as new central nervous system drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 1: 187–197
Doupnik C. A., Davidson N., Lester H. A. and Kofuji P. (1997) RGS proteins reconstitute the rapid gating kinetics of gbetagamma-activated inwardly rectifying K+ channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 10461–10466
Saitoh O., Kubo Y., Miyatani Y., Asano T. and Nakata H. (1997) RGS8 accelerates G-protein-mediated modulation of K+ currents. Nature 390: 525–529
Buenemann M. and Hosey M. M. (1998) Regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) proteins constitutively activate Gbeta/gamma-gated potassium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 31186–31190
Chuang H.-H., Yu M., Jan Y. N. and Jan L. Y. (1998) Evidence that the nucleotide exchange and hydrolysis cycle of G proteins cause acute desensitization of G-protein gated inward rectifier K+ channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 11727–11732
Herlitze S., Ruppersberg J. P. and Mark M. D. (1999) New roles for RGS2, 5 and 8 on the ratio-dependent modulation of recombinant GIRK channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J. Physiol. 517: 341–352
Saitoh O., Kubo Y., Odagiri M., Ichikawa M., Kanato Y. and Sekine T. (1999) RGS7 and RGS8 differentially accelerate G Protein-mediated modulation of K+ currents. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 9899–9904
Snow B. E., Krumins A. M., Brothers G. M., Lee S.-F., Wall M. A., Chung S. et al. (1998) A G protein gamma subunit-like domain shared between RGS11 and other RGS proteins specifies binding to Gbeta5 subunits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 13307–13312
Snow B. E., Betts L., Mangion J., Sondek J. and Siderovski D. P. (1999) Fidelity of G protein beta-subunit association by the G protein gamma-subunit-like domains of RGS6, RGS7, and RGS11. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 6489–6494
Makino E. R., Handy J. W., Li T. and Arshavsky V. Y. (1999) The GTPase activating factor for transducin in rod photoreceptors is the complex between RGS9 and type 5 G protein beta subunit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 1947–1952
Levay K., Cabrera J. L., Satpaev D. K. and Slepak V. Z. (1999) Gbeta5 prevents the RGS7-Galpha-o interaction through binding to a distinct Ggamma-like domain found in RGS7 and other RGS proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 2503–2507
Hu G. and Wensel T. G. (2002) R9AP, a membrane anchor for the photoreceptor GTPase accelerating protein, RGS9-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99: 9755–9760
Lishko P. V., Martemyanov K. A., Hopp J. A. and Arshavsky V. Y. (2002) Specific binding of RGS9-Gbeta 5L to protein anchor in photoreceptor membranes greatly enhances its catalytic activity. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 24376–24381
Schiff M. L., Siderovski D. P., Jordan J. D., Brothers G., Snow B., De Vries L. et al. (2000) Tyrosine kinase-dependent recruitment of RGS12 to the N-type calcium channel. Nature 408: 723–727
Snow B. E., Hall R. A., Krumins A. M., Brothers G. M., Bouchard D., Brothers C. A. et al. (1998) GTPase activating specificity of RGS12 and binding specificity of an alternatively spliced PDZ (PSD-95/Dlg/ZO-1) domain. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 17749–17755
Ponting C. P. (1999) Raf-like Ras/Rap-binding domains in RGS12 and still life like signalling proteins. J. Mol. Med. 77: 695–698
Traver S., Bidot C., Spassky N., Baltauss T., De Tand M. F., Thomas J. L. et al. (2000) RGS14 is a novel Rap effector that preferentially regulates the GTPase activity of galphao. Biochem. J. 350: 19–29
Kimple R. J., De Vries L., Tronchere H., Behe C. I., Morris R. A., Farquhar M. G. et al. (2001) RGS12 and RGS14 GoLoco motifs are Galpha (i) interaction sites with guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor activity. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 29275–29281
Kimple R. J., Kimple M. E., Betts L., Sondek J. and Siderovski D. P. (2002) Structural determinants for GoLoco-induced inhibition of nucleotide release by Galpha subunits. Nature 416: 878–881
Willard F. S., Kimple R. J. and Siderovski D. P. (2004) Return of the GDI: the GoLoco motif in cell division. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 73: 925–951
Fukuhara S., Chikumi H. and Gutkind J. S. (2000) Leukemia-associated rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (LARG) links heterotrimeric G proteins of the G(12) family to Rho [In Process Citation]. FEBS Lett. 485: 183–188
Ferguson S. S. (2001) Evolving concepts in G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis: the role in receptor desensitization and signaling. Pharmacol. Rev. 53: 1–24
Carman C. V., Parent J. L., Day P. W., Pronin A. N., Sternweis P. M., Wedegaertner P. B. et al. (1999) Selective regulation of Galpha(q/11) by an RGS domain in the G protein-coupled receptor kinase, GRK2. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 34483–34492
Dhami G. K., Dale L. B., Anborgh P. H., O'Connor-Halligan K. E., Sterne-Marr R. and Ferguson S. S. (2004) G Protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 regulator of G protein signaling homology domain binds to both metabotropic glutamate receptor 1a and Galphaq to attenuate signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 16614–16620
Iacovelli L., Capobianco L., Iula M., Di Giorgi Gerevini V., Picascia A., Blahos J. et al. (2004) Regulation of mGlu4 metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling by type-2 G-protein coupled receptor kinase (GRK2). Mol. Pharmacol. 65: 1103–1110
Kohout T. A. and Lefkowitz R. J. (2003) Regulation of G protein-coupled receptor kinases and arrestins during receptor desensitization. Mol. Pharmacol. 63: 9–18
Lorenz K., Lohse M. J. and Quitterer U. (2003) Protein kinase C switches the Raf kinase inhibitor from Raf-1 to GRK-2. Nature 426: 574–579
Yeung K., Seitz T., Li S., Janosch P., McFerran B., Kaiser C. et al. (1999) Suppression of Raf-1 kinase activity and MAP kinase signalling by RKIP. Nature 401: 173–177
Spink K. E., Polakis P. and Weis W. I. (2000) Structural basis of the Axin-adenomatous polyposis coli interaction. EMBO J. 19: 2270–2279
Berridge M. J. (1987) Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 56: 159–193
Saunders C. M., Larman M. G., Parrington J., Cox L. J., Royse J., Blayney L. M. et al. (2002) PLC zeta: a sperm-specific trigger of Ca(2+) oscillations in eggs and embryo development. Development 129: 3533–3544
Smrcka A. V., Hepler J. R., Brown K. O. and Sternweis P. C. (1991) Regulation of polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C activity by purified Gq. Science 251: 804–807
Taylor S. J., Chae H. Z., Rhee S. G. and Exton J. H. (1991) Activation of the beta 1 isozyme of phospholipase C by alpha subunits of the Gq class of G proteins. Nature 350: 516–518
Waldo G. L., Boyer J. L., Morris A. J. and Harden T. K. (1991) Purification of an AlF4- and G-protein beta gamma-subunit-regulated phospholipase C-activating protein. J. Biol. Chem. 266: 14217–14225
Wu D. Q., Lee C. H., Rhee S. G. and Simon M. I. (1992) Activation of phospholipase C by the alpha subunits of the Gq and G11 proteins in transfected Cos-7 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 1811–1817
Blank J. L., Brattain K. A. and Exton J. H. (1992) Activation of cytosolic phosphoinositide phospholipase C by G-protein beta gamma subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 23069–23075
Camps M., Carozzi A., Schnabel P., Scheer A., Parker P. J. and Gierschik P. (1992) Isozyme-selective stimulation of phospholipase C-beta 2 by G protein beta gamma-subunits. Nature 360: 684–686
Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G. and Carpenter G. (1989) Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II independently of receptor internalization and extracellular calcium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 1568–1572
Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G. and Hunter T. (1989) Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell 57: 1109–1122
Rhee S. G. and Choi K. D. (1992) Regulation of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C isozymes. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 12393–12396
Kim Y. H., Park T. J., Lee Y. H., Baek K. J., Suh P. G., Ryu S. H. et al. (1999) Phospholipase C-delta1 is activated by capacitative calcium entry that follows phospholipase C-beta activation upon bradykinin stimulation. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 26127–26134
Baek K. J., Kang S., Damron D. and Im M. (2001) Phospholipase Cdelta1 is a guanine nucleotide exchanging factor for transglutaminase II (Galpha h) and promotes alpha 1B-adrenoreceptor-mediated GTP binding and intracellular calcium release. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 5591–5597
Shibatohge M., Kariya K., Liao Y., Hu C. D., Watari Y., Goshima M. et al. (1998) Identification of PLC210, a Caenorhabditis elegans phospholipase C, as a putative effector of Ras. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 6218–6222
Kelley G. G., Reks S. E., Ondrako J. M. and Smrcka A. V. (2001) Phospholipase C(epsilon): a novel Ras effector. EMBO J. 20: 743–754
Lopez I., Mak E. C., Ding J., Hamm H. E. and Lomasney J. W. (2001) A novel bifunctional phospholipase c that is regulated by Galpha 12 and stimulates the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 2758–2765
Song C., Hu C. D., Masago M., Kariyai K., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Shibatohge M. et al. (2001) Regulation of a novel human phospholipase C, PLCepsilon, through membrane targeting by Ras. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 2752–2757
Wing M. R., Snyder J. T., Sondek J. and Harden T. K. (2003) Direct activation of phospholipase C-epsilon by Rho. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 41253–41258
Schmidt M., Evellin S., Weernink P. A., von Dorp F., Rehmann H., Lomasney J. W. et al. (2001) A new phospholipase-C-calcium signalling pathway mediated by cyclic AMP and a Rap GTPase. Nat. Cell Biol. 3: 1020–1024
Hains M. D., Siderovski D. P. and Harden T. K. (2004) Application of RGS box proteins to evaluate G-protein selectivity in receptor-promoted signaling. Methods Enzymol 389: 71–88
Kelley G. G., Reks S. E. and Smrcka A. V. (2004) Hormonal regulation of phospholipase Cepsilon through distinct and overlapping pathways involving G12 and Ras family G-proteins. Biochem. J. 378: 129–139
Song C., Satoh T., Edamatsu H., Wu D., Tadano M., Gao X. et al. (2002) Differential roles of Ras and Rap1 in growth factor-dependent activation of phospholipase C epsilon. Oncogene 21: 8105–8113
Jin T. G., Satoh T., Liao Y., Song C., Gao X., Kariya K. et al. (2001) Role of the CDC25 homology domain of phospholipase Cepsilon in amplification of Rap1-dependent signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 30301–30307
Wing M. R., Bourdon D. M. and Harden T. K. (2003) PLC-epsilon: a shared effector protein in Ras-, Rho- and Gαβγ-mediated signaling. Mol. Interv. 3: 273–280
Seifert J. P., Wing M. R., Snyder J. T., Gershburg S., Sondek J. and Harden T. K. (2004) RhoA activates purified phospholipase C-epsilon by a guanine nucleotide-dependent mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 279:47992–47997
Illenberger D., Schwald F., Pimmer D., Binder W., Maier G., Dietrich A. et al. (1998) Stimulation of phospholipase C-beta2 by the Rho GTPases Cdc42Hs and Rac1. EMBO J. 17: 6241–6249
Illenberger D., Walliser C., Nurnberg B., Diaz Lorente M. and Gierschik P. (2003) Specificity and structural requirements of phospholipase C-beta stimulation by Rho GTPases versus G protein beta gamma dimers. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 3006–3014
Evellin S., Nolte J., Tysack K., vom Dorp F., Thiel M., Weernink P. A. et al. (2002) Stimulation of phospholipase C-epsilon by the M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediated by cyclic AMP and the GTPase Rap2B. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 16805–16813
vom Dorp F., Sari A. Y., Sanders H., Keiper M., Weernink P. A., Jakobs K. H. et al. (2004) Inhibition of phospholipase C-epsilon by Gi-coupled receptors. Cell Signal. 16: 921–928
de Rooij J., Zwartkruis F. J., Verheijen M. H., Cool R. H., Nijman S. M., Wittinghofer A. et al. (1998) Epac is a Rap1 guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor directly activated by cyclic AMP. Nature 396: 474–477
Springett G. M., Kawasaki H. and Spriggs D. R. (2004) Nonkinase second-messenger signaling: new pathways with new promise. Bioessays 26: 730–738
Stope M. B., Vom Dorp F., Szatkowski D., Bohm A., Keiper M., Nolte J. et al. (2004) Rap2B-dependent stimulation of phospholipase C-epsilon by epidermal growth factor receptor mediated by c-Src phosphorylation of RasGRP3. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24: 4664–4676
Ross C. A., MacCumber M. W., Glatt C. E. and Snyder S. H. (1989) Brain phospholipase C isozymes: differential mRNA localizations by in situ hybridization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 2923–2927
Kim D., Jun K. S., Lee S. B., Kang N. G., Min D. S., Kim Y. H. et al. (1997) Phospholipase C isozymes selectively couple to specific neurotransmitter receptors. Nature 389: 290–293
Wu D., Tadano M., Edamatsu H., Masago-Toda M., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Terashima T. et al. (2003) Neuronal lineage-specific induction of phospholipase Cepsilon expression in the developing mouse brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 17: 1571–1580
Clandinin T. R., DeModena J. A. and Sternberg P. W. (1998) Inositol trisphosphate mediates a RAS-independent response to LET-23 receptor tyrosine kinase activation in C. elegans. Cell 92: 523–533
Bui Y. K. and Sternberg P. W. (2002) Caenorhabditis elegans inositol 5-phosphatase homolog negatively regulates inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate signaling in ovulation. Mol. Biol. Cell 13: 1641–1651
Kariya K., Kim Bui Y., Gao X., Sternberg P. W. and Kataoka T. (2004) Phospholipase Cepsilon regulates ovulation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol. 274: 201–210
Otsuki M., Fukami K., Kohno T., Yokota J. and Takenawa T. (1999) Identification and characterization of a new phospholipase C-like protein, PLC-L(2). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 266: 97–103
Kurosaki T., Maeda A., Ishiai M., Hashimoto A., Inabe K. and Takata M. (2000) Regulation of the phospholipase C-gamma2 pathway in B cells. Immunol. Rev. 176: 19–29
Takenaka K., Fukami K., Otsuki M., Nakamura Y., Kataoka Y., Wada M. et al. (2003) Role of phospholipase C-L2, a novel phospholipase C-like protein that lacks lipase activity, in B-cell receptor signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23: 7329–7338
Cismowski M. J., Takesono A., Ma C., Lizano J. S., Xie X., Fuernkranz H. et al. (1999) Genetic screens in yeast to identify mammalian nonreceptor modulators of G-protein signaling. Nat. Biotechnol. 17: 878–883
Kemppainen R. J. and Behrend E. N. (1998) Dexamethasone rapidly induces a novel ras superfamily member-related gene in AtT-20 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 3129–3131
Cismowski M. J., Ma C., Ribas C., Xie X., Spruyt M., Lizano J. S. et al. (2000) Activation of heterotrimeric G-protein signaling by a ras-related protein. Implications for signal integration. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 23421–23424
Graham T. E., Prossnitz E. R. and Dorin R. I. (2002) Dexras1/AGS-1 inhibits signal transduction from the Gi-coupled formyl peptide receptor to Erk-1/2 MAP kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 10876–10882
Takesono A., Nowak M. W., Cismowski M., Duzic E. and Lanier S. M. (2002) Activator of G-protein signaling 1 blocks GIRK channel activation by a G-protein-coupled receptor: apparent disruption of receptor signaling complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 13827–13830
Fang M., Jaffrey S. R., Sawa A., Ye K., Luo X. and Snyder S. H. (2000) Dexras1: a G protein specifically coupled to neuronal nitric oxide synthase via CAPON. Neuron 28: 183–193
Cheng H. Y., Obrietan K., Cain S. W., Lee B. Y., Agostino P. V., Joza N. A. et al. (2004) Dexras1 potentiates photic and suppresses nonphotic responses of the circadian clock. Neuron 43: 715–728
Takahashi H., Umeda N., Tsutsumi Y., Fukumura R., Ohkaze H., Sujino M. et al. (2003) Mouse dexamethasone-induced RAS protein 1 gene is expressed in a circadian rhythmic manner in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Brain Res. Mol. Brain. Res. 110: 1–6
Tall G. G., Krumins A. M. and Gilman A. G. (2003) Mammalian Ric-8A (Synembryn) is a heterotrimeric Galpha protein guanine nucleotide exchange factor. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 8356–8362
Granderath S., Stollewerk A., Greig S., Goodman C. S., O'Kane C. J. and Klambt C. (1999) loco encodes an RGS protein required for Drosophila glial differentiation. Development 126: 1781–1791
Siderovski D. P., Diverse-Pierluissi M. A. and DeVries L. (1999) The GoLoco motif: a G alpha i/o binding motif and potential guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24: 340–341
Takesono A., Cismowski M. J., Ribas C., Bernard M., Chung P., Hazard S. III et al. (1999) Receptor-independent activators of heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 33202–33205
Colombo K., Grill S. W., Kimple R. J., Willard F. S., Siderovski D. P. and Gonczy P. (2003) Translation of polarity cues into asymmetric spindle positioning in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Science 300: 1957–1961
Gotta M., Dong Y., Peterson Y. K., Lanier S. M. and Ahringer J. (2003) Asymmetrically distributed C. elegans homologs of AGS3/PINS control spindle position in the early embryo. Curr. Biol. 13: 1029–1037
Srinivasan D. G., Fisk R. M., Xu H. and van den Heuvel S. (2003) A complex of LIN-5 and GPR proteins regulates G protein signaling and spindle function in C. elegans. Genes Dev. 17: 1225–1239
Schaefer M., Shevchenko A., Shevchenko A. and Knoblich J. A. (2000) A protein complex containing Inscuteable and the Galpha-binding protein Pins orients asymmetric cell divisions in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 10: 353–362
Yu F., Morin X., Cai Y., Yang X. and Chia W. (2000) Analysis of partner of inscuteable, a novel player of Drosophila asymmetric divisions, reveals two distinct steps in inscuteable apical localization. Cell 100: 399–409
Luo Y. and Denker B. M. (1999) Interaction of heterotrimeric G protein Galphao with Purkinje cell protein-2. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 10685–10688
Zhang X., Zhang H. and Oberdick J. (2002) Conservation of the developmentally regulated dendritic localization of a Purkinje cell-specific mRNA that encodes a G-protein modulator: comparison of rodent and human Pcp2(L7) gene structure and expression. Brain Res. Mol. Brain. Res. 105: 1–10
Meng J., Glick J. L., Polakis P. and Casey P. J. (1999) Functional interaction between Galpha(z) and Rap1GAP suggests a novel form of cellular cross-talk. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 36663–36669
Mochizuki N., Ohba Y., Kiyokawa E., Kurata T., Murakami T., Ozaki T. et al. (1999) Activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway by an isoform of rap1GAP associated with G alpha(i). Nature 400: 891–894
Kimple R. J., Willard F. S., Hains M. D., Jones M. B., Nweke G. K. and Siderovski D. P. (2004) Guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor activity of the triple GoLoco motif protein G18: alanine-to-aspartate mutation restores function to an inactive second GoLoco motif. Biochem. J. 378: 801–808
Cao X., Cismowski M. J., Sato M., Blumer J. B. and Lanier S. M. (2004) Identification and characterization of AGS4: a protein containing three G-protein regulatory motifs that regulate the activation state of Gialpha. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 27567–27574
Mochizuki N., Cho G., Wen B. and Insel P. A. (1996) Identification and cDNA cloning of a novel human mosaic protein, LGN, based on interaction with G alpha i2. Gene 181: 39–43
Natochin M., Gasimov K. G. and Artemyev N. O. (2001) Inhibition of GDP/GTP exchange on G alpha subunits by proteins containing G-protein regulatory motifs. Biochemistry 40: 5322–5328
Du Q., Taylor L., Compton D. A. and Macara I. G. (2002) LGN blocks the ability of NuMA to bind and stabilize microtubules. A mechanism for mitotic spindle assembly regulation. Curr. Biol. 12: 1928–1933
Natochin M., Lester B. R., Peterson Y. K., Bernard M. L., Lanier S. M. and Artemyev N. O. (2000) AGS3 inhibits GDP dissociation from Galpha subunits of Gi family and rhodopsin-dependent activation of transducin. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 40981–40985
Adhikari A. and Sprang S. R. (2003) Thermodynamic characterization of the binding of activator of G protein signaling 3 (AGS3) and peptides derived from AGS3 with Galpha-i1. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 51825–51832
Du Q., Stukenberg P. T. and Macara I. G. (2001) A mammalian partner of inscuteable binds NuMA and regulates mitotic spindle organization. Nat. Cell. Biol. 3: 1069–1075
Dohlman H. G. (2002) G proteins and pheromone signaling. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 64: 129–152
Chan R. K. and Otte C. A. (1982) Isolation and genetic analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants supersensitive to G1 arrest by a factor and alpha factor pheromones. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2: 11–20
Konijn T. M., van de Meene J. G., Chang Y. Y., Barkley D. S. and Bonner J. T. (1969) Identification of adenosine-3′,5′-monophosphate as the bacterial attractant for myxamoebae of Dictyostelium discoideum. J. Bacteriol. 99: 510–512
Iijima M., Huang Y. E. and Devreotes P. (2002) Temporal and spatial regulation of chemotaxis. Dev. Cell 3: 469–478
Wettschureck N., Moers A. and Offermanns S. (2004) Mouse models to study G-protein-mediated signaling. Pharmacol. Ther. 101: 75–89
Ullah H., Chen J. G., Young J. C., Im K. H., Sussman M. R. and Jones A. M. (2001) Modulation of cell proliferation by heterotrimeric G protein in Arabidopsis. Science 292: 2066–2069
Wang X. Q., Ullah H., Jones A. M. and Assmann S. M. (2001) G protein regulation of ion channels and abscisic acid signaling in Arabidopsis guard cells. Science 292: 2070–2072
Jones A. M. (2002) G-protein-coupled signaling in Arabidopsis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5: 402–407
Apone F., Alyeshmerni N., Wiens K., Chalmers D., Chrispeels M. J. and Colucci G. (2003) The G-protein-coupled receptor GCR1 regulates DNA synthesis through activation of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Plant Physiol. 133: 571–579
Zhao J. and Wang X. (2004) Arabidopsis phospholipase Dalpha1 interacts with the heterotrimeric G-protein alphasubunit through a motif analogous to the DRY motif in G-protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem 279: 1794–1800
Chen J.-G., Willard F. S., Huang J., Liang J., Chasse S. A., Jones A. M. et al. (2003) A seven-transmembrane RGS protein that modulates plant cell proliferation. Science 301: 1728–1731
Willard F. S. and Siderovski D. P. (2004) Purification and in vitro functional analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana regulator of G-protein signaling-1. Methods Enzymol. 389: 320–338
Chen J. G. and Jones A. M. (2004) AtRGS1 function in Arabidopsis thaliana. Methods Enzymol. 389: 338–350
Wang Q., Liu M., Mullah B., Siderovski D. P. and Neubig R. R. (2002) Receptor-selective effects of endogenous RGS3 and RGS5 to regulate mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 24949–24958
Xu X., Zeng W., Popov S., Berman D. M., Davignon I., Yu K. et al. (1999) RGS proteins determine signaling specificity of Gq-coupled receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 3549–3556
Zeng W., Xu X., Popov S., Mukhopadhyay S., Chidiac P., Swistok J. et al. (1998) The N-terminal domain of RGS4 confers receptor-selective inhibition of G protein signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 34687–34690
Bernstein L. S., Ramineni S., Hague C., Cladman W., Chidiac P., Levey A. I. et al. (2004) RGS2 binds directly and selectively to the M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor third intracellular loop to modulate Gq/11alpha signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 21248–21256
Zhong H., Wade S. M., Woolf P. J., Linderman J. J., Traynor J. R. and Neubig R. R. (2003) A spatial focusing model for G protein signals. Regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) protien-mediated kinetic scaffolding. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 7278–7284
Worby C. A. and Dixon J. E. (2002) Sorting out the cellular functions of sorting nexins. Nat. Rev. Mo.l Cell. Biol. 3: 919–931
Popov S. G., Krishna U. M., Falck J. R. and Wilkie T. M. (2000) Ca2+/Calmodulin reverses phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent inhibition of regulators of G protein-signaling GTPase-activating protein activity. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 18962–18968
Tu Y. and Wilkie T. M. (2004) Allosteric regulation of GAP activity by rhospholipids in regulators of G-protein signaling. Methods Enzymol. 389: 89–1005
Ishii M. and Kurachi Y. (2004) Assays of RGS protein modulation by phosphatidylinositides and calmodulin. Methods Enzymol. 389: 105–118
Tu Y., Popov S., Slaughter C. and Ross E. M. (1999) Palmitoylation of a conserved cysteine in the regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) domain modulates the GTPase-activating activity of RGS4 and RGS10. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 38260–38267
Jones T. L. (2004) Role of palmitoylation in RGS protein function. Methods Enzymol. 389: 33–55
Ishii M., Inanobe A. and Kurachi Y. (2002) PIP3 inhibition of RGS protein and its reversal by Ca2+/calmodulin mediate voltage-dependent control of the G protein cycle in a cardiac K+ channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99: 4325–4330
Roy A. A., Lemberg K. E. and Chidiac P. (2003) Recruitment of RGS2 and RGS4 to the plasma membrane by G proteins and receptors reflects functional interactions. Mol. Pharmacol. 64: 587–593
Druey K. M., Sullivan B. M., Brown D., Fischer E. R., Watson N., Blumer K. J. et al. (1998) Expression of GTPase-deficient Gialpha2 results in translocation of cytoplasmic RGS4 to the plasma membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 18405–18410
Krumins A. M., Barker S. A., Huang C., Sunahara R. K., Yu K., Wilkie T. M. et al. (2004) Differentially regulated expression of endogenous RGS4 and RGS7. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 2593–2599
Wise A., Jupe S. C. and Rees S. (2004) The identification of ligands at orphan G-protein coupled receptors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 44: 43–66
Coursol S., Fan L. M., Le Stunff H., Spiegel S., Gilroy S. and Assmann S. M. (2003) Sphingolipid signalling in Arabidopsis guard cells involves heterotrimeric G proteins. Nature 423: 651–654
Chun J., Goetzl E. J., Hla T., Igarashi Y., Lynch K. R., Moolenaar W. et al. (2002) International Union of Pharmacology. XXXIV. Lysophospholipid receptor nomenclature. Pharmacol Rev 54: 265–269
Gonczy P. (2002) Mechanisms of spindle positioning: focus on flies and worms. Trends Cell Biol. 12: 332–339
Macara I. G. (2004) Parsing the polarity code. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 5: 220–231
Wodarz A. and Huttner W. B. (2003) Asymmetric cell division during neurogenesis in Drosophila and vertebrates. Mech. Dev. 120: 1297–1309
Chia W. and Yang X. (2002) Asymmetric division of Drosophila neural progenitors. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 12: 459–464
Vaessin H., Grell E., Wolff E., Bier E., Jan L. Y. and Jan Y. N. (1991) Prospero is expressed in neuronal precursors and encodes a nuclear protein that is involved in the control of axonal outgrowth in Drosophila. Cell 67: 941–953
Doe C. Q., Chu-LaGraff Q., Wright D. M. and Scott M. P. (1991) The prospero gene specifies cell fates in the Drosophila central nervous system. Cell 65: 451–464
Knoblich J. A., Jan L. Y. and Jan Y. N. (1995) Asymmetric segregation of Numb and Prospero during cell division. Nature 377: 624–627
Hirata J., Nakagoshi H., Nabeshima Y. and Matsuzaki F. (1995) Asymmetric segregation of the homeodomain protein Prospero during Drosophila development. Nature 377: 627–630
Spana E. P. and Doe C. Q. (1995) The prospero transcription factor is asymmetrically localized to the cell cortex during neuroblast mitosis in Drosophila. Development 121: 3187–3195
Schuldt A. J., Adams J. H., Davidson C. M., Micklem D. R., Haseloff J., St Johnston D. et al. (1998) Miranda mediates asymmetric protein and RNA localization in the developing nervous system. Genes Dev. 12: 1847–1857
Li P., Yang X., Wasser M., Cai Y. and Chia W. (1997) Inscuteable and Staufen mediate asymmetric localization and segregation of prospero RNA during Drosophila neuroblast cell divisions. Cell 90: 437–447
Broadus J., Fuerstenberg S. and Doe C. Q. (1998) Staufen-dependent localization of prospero mRNA contributes to neuroblast daughter-cell fate. Nature 391: 792–795
Shen C. P., Jan L. Y. and Jan Y. N. (1997) Miranda is required for the asymmetric localization of Prospero during mitosis in Drosophila. Cell 90: 449–458
Ikeshima-Kataoka H., Skeath J. B., Nabeshima Y., Doe C. Q. and Matsuzaki F. (1997) Miranda directs Prospero to a daughter cell during Drosophila asymmetric divisions. Nature 390: 625–629
Guo M., Jan L. Y. and Jan Y. N. (1996) Control of daughter cell fates during asymmetric division: interaction of Numb and Notch. Neuron 17: 27–41
Frise E., Knoblich J. A., Younger-Shepherd S., Jan L. Y. and Jan Y. N. (1996) The Drosophila Numb protein inhibits signaling of the Notch receptor during cell-cell interaction in sensory organ lineage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 11925–11932
Lu B., Rothenberg M., Jan L. Y. and Jan Y. N. (1998) Partner of Numb colocalizes with Numb during mitosis and directs Numb asymmetric localization in Drosophila neural and muscle progenitors. Cell 95: 225–235
Berdnik D., Torok T., Gonzalez-Gaitan M. and Knoblich J. A. (2002) The endocytic protein alpha-Adaptin is required for numb-mediated asymmetric cell division in Drosophila. Dev. Cell 3: 221–231
Kraut R. and Campos-Ortega J. A. (1996) Inscuteable, a neural precursor gene of Drosophila, encodes a candidate for a cytoskeleton adaptor protein. Deve. Biol. 174: 65–81
Kraut R., Chia W., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. and Knoblich J. A. (1996) Role of inscuteable in orienting asymmetric cell divisions in Drosophila. Nature 383: 50–55
Schober M., Schaefer M. and Knoblich J. A. (1999) Bazooka recruits Inscuteable to orient asymmetric cell divisions in Drosophila neuroblasts. Nature 402: 548–551
Schaefer M. and Knoblich J. A. (2001) Protein localization during asymmetric cell division. Exp. Cell. Res. 271: 66–74
Schaefer M., Petronczki M., Dorner D., Forte M. and Knoblich J. A. (2001) Heterotrimeric G proteins direct two modes of asymmetric cell division in the Drosophila nervous system. Cell 107: 183–194
Kaushik R., Yu F., Chia W., Yang X. and Bahri S. (2003) Subcellular localization of LGN during mitosis: evidence for its cortical localization in mitotic cell culture systems and its requirement for normal cell cycle progression. Mol. Biol. Cell. 14: 3144–3155
Jiang X., Wilford C., Duensing S., Munger K., Jones G. and Jones D. (2001) Participation of Survivin in mitotic and apoptotic activities of normal and tumor-derived cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 83: 342–354
Cai Y., Chia W. and Yang X. (2001) A family of snail-related zinc finger proteins regulates two distinct and parallel mechanisms that mediate Drosophila neuroblast asymmetric divisions. EMBO J. 20: 1704–1714
Izumi Y., Ohta N., Itoh-Furuya A., Fuse N. and Matsuzaki F. (2004) Differential functions of G protein and Baz-aPKC signaling pathways in Drosophila neuroblast asymmetric division. J. Cell Biol. 164: 729–738
Fuse N., Hisata K., Katzen A. L. and Matsuzaki F. (2003) Heterotrimeric G proteins regulate daughter cell size asymmetry in Drosophila neuroblast divisions. Curr. Biol. 13: 947–954
Yu F., Cai Y., Kaushik R., Yang X. and Chia W. (2003) Distinct roles of Galpha-i and Gbeta13F subunits of the heterotrimeric G protein complex in the mediation of Drosophila neuroblast asymmetric divisions. J. Cell Biol. 162: 623–633
Fuja T. J., Schwartz P. H., Darcy D. and Bryant P. J. (2004) Asymmetric localization of LGN but not AGS3, two homologs of Drosophila pins, in dividing human neural progenitor cells. J Neurosci Res 75: 782–793
Hartenstein V. and Posakony J. W. (1989) Development of adult sensilla on the wing and notum of Drosophila melanogaster. Development 107: 389–405
Gho M., Bellaiche Y. and Schweisguth F. (1999) Revisiting the Drosophila microchaete lineage: a novel intrinsically asymmetric cell division generates a glial cell. Development 126: 3573–3584
Rhyu M. S., Jan L. Y. and Jan Y. N. (1994) Asymmetric distribution of numb protein during division of the sensory organ precursor cell confers distinct fates to daughter cells. Cell 76: 477–491
Cai Y., Yu F., Lin S., Chia W. and Yang X. (2003) Apical complex genes control mitotic spindle geometry and relative size of daughter cells in Drosophila neuroblast and pI asymmetric divisions. Cell 112: 51–62
Roegiers F. (2003) Insights into mRNA transport in neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100: 1465–1466
Bellaiche Y., Radovic A., Woods D. F., Hough C. D., Parmentier M. L., O'Kane C. J. et al. (2001) The partner of Inscuteable/Discs-large complex is required to establish planar polarity during asymmetric cell division in Drosophila. Cell 106: 355–366
Malbon C. C. (2004) Frizzleds: new members of the superfamily of G-protein-coupled receptors. Front. Biosci. 9: 1048–1058
Bellaiche Y., Gho M., Kaltschmidt J. A., Brand A. H. and Schweisguth F. (2001) Frizzled regulates localization of cell-fate determinants and mitotic spindle rotation during asymmetric cell division. Nat. Cell. Biol. 3: 50–57
Gonczy P., Grill S., Stelzer E. H., Kirkham M. and Hyman A. A. (2001) Spindle positioning during the asymmetric first cell division of Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Novartis Found. Symp. 237: 164–175
Knoblich J. A. (2001) Asymmetric cell division during animal development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2: 11–20
Schneider S. Q. and Bowerman B. (2003) Cell polarity and the cytoskeleton in the Caenorhabditis elegans zygote. Annu. Rev. Genet. 37: 221–249
Kemphues K. J., Priess J. R., Morton D. G. and Cheng N. S. (1988) Identification of genes required for cytoplasmic localization in early C. elegans embryos. Cell 52: 311–320
Etemad-Moghadam B., Guo S. and Kemphues K. J. (1995) Asymmetrically distributed PAR-3 protein contributes to cell polarity and spindle alignment in early C. elegans embryos. Cell 83: 743–752
Hung T. J. and Kemphues K. J. (1999) PAR-6 is a conserved PDZ domain-containing protein that colocalizes with PAR-3 in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Development 126: 127–135
Tabuse Y., Izumi Y., Piano F., Kemphues K. J., Miwa J. and Ohno S. (1998) Atypical protein kinase C cooperates with PAR-3 to establish embryonic polarity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development 125: 3607–3614
Gotta M., Abraham M. C. and Ahringer J. (2001) CDC-42 controls early cell polarity and spindle orientation in C. elegans. Curr Biol 11: 482–488
Gotta M. and Ahringer J. (2001) Distinct roles for Galpha and Gbetagamma in regulating spindle position and orientation in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Nat. Cell. Biol. 3: 297–300
Watts J. L., Morton D. G., Bestman J. and Kemphues K. J. (2000) The C. elegans par-4 gene encodes a putative serinethreonine kinase required for establishing embryonic asymmetry. Development 127}: 1467–1475
Zwaal R. R., Ahringer J., van Luenen H. G., Rushforth A., Anderson P. and Plasterk R. H. (1996) G proteins are required for spatial orientation of early cell cleavages in C. elegans embryos. Cell 86: 619–629
Afshar K., Willard F. S., Colombo K., Johnston C. A., McCudden C. R., Siderovski D. P. et al. (2004) RIC-8 is required for GPR-1/2-dependent G-alpha function during asymmetric division of C. elegans embryos. Cell 119: 219–230
Grill S. W., Howard J., Schaffer E., Stelzer E. H. K. and Hyman A. A. (2003) The distribution of active force generators controls mitotic spindle position. Science 301: 518–521
Verdi J. M., Schmandt R., Bashirullah A., Jacob S., Salvino R., Craig C. G. et al. (1996) Mammalian NUMB is an evolutionarily conserved signaling adapter protein that specifies cell fate. Curr. Biol. 6: 1134–1145
Cayouette M. and Raff M. (2002) Asymmetric segregation of Numb: a mechanism for neural specification from Drosophila to mammals. Nat. Neurosci. 5: 1265–1269
Blumer J. B., Chandler L. J. and Lanier S. M. (2002) Expression analysis and subcellular distribution of the two G-protein regulators AGS3 and LGN indicate distinct functionality. Localization of LGN to the midbody during cytokinesis. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 15897–15903
Cleveland D. W. (1995) NuMA: a protein involved in nuclear structure, spindle assembly, and nuclear re-formation. Trends Cell Biol. 5: 60–64
Yu F., Ong C. T., Chia W. and Yang X. (2002) Membrane targeting and asymmetric localization of Drosophila partner of inscuteable are discrete steps controlled by distinct regions of the protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22: 4230–4240
Broadus J. and Doe C. Q. (1997) Extrinsic cues, intrinsic cues and microfilaments regulate asymmetric protein localization in Drosophila neuroblasts. Curr. Biol. 7: 827–835
Qian X., Goderie S. K., Shen Q., Stern J. H. and Temple S. (1998) Intrinsic programs of patterned cell lineages in isolated vertebrate CNS ventricular zone cells. Development 125: 3143–3152
Miller K. G. and Rand J. B. (2000) A role for RIC-8 (Synembryn) and GOA-1 (Go-alpha) in regulating a subset of centrosome movements during early embryogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 156: 1649–1660
Couwenbergs C., Spilker A. C. and Gotta M. (2004) Control of embryonic spindle positioning and G-alpha activity by C. elegans RIC-8. Curr. Biol. 14: 1871–1876
Hess H. A., Roper J.-C., Grill S. W. and Koelle M. R. (2004) RGS-7 completes a receptor-independent heterotrimeric G protein cycle to asymmetrically regulate mitotic spindle positioning in C. elegans. Cell 119: 209–218
Martin-McCaffrey L., Willard F. S., Oliveira-dos-Santos A. J., Natale D. R. C., Snow B. E., Kimple R. J. et al. (2004) RGS14 is a mitotic spindle protein essential from the first division of the mammalian zygote. Developmental Cell 7: 763–769
Martin-McCaffrey L., Willard F. S., Pajak A., Dagnino L., Siderovski D. P. and D'souza S. J. A. (2004) Analysis of interactions between Regulator of G-protein Signaling-14 and microtubules. Methods Enzymol. 390: 240–258
Chen N.-F., Yu J.-Z., Skiba N. P., Hamm H. E. and Rasenick M. M. (2003) A specific domain of Gialpha required for the transactivation of Gialpha by tubulin is implicated in the organization of cellular microtubules. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 15285–15290
Popova J. S. and Rasenick M. M. (2003) Gbg mediates the interplay between tubulin dimers and microtubules in the modulation of Gq signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 34299–34308
Roychowdhury S., Panda D., Wilson L. and Rasenick M. M. (1999) G protein alpha subunits activate tubulin GTPase and modulate microtubule polymerization dynamics. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 13485–13490
Roychowdhury S. and Rasenick M. M. (1997) G Protein beta 1gamma 2 subunits promote microtubule assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 31576–31581
Wang N., Yan K. and Rasenick M. (1990) Tubulin binds specifically to the signal-transducing proteins, Gs alpha and Gi alpha 1. J. Biol. Chem. 265: 1239–1242
Sarma T., Voyno-Yasenetskaya T., Hope T. J. and Rasenick M. M. (2003) Heterotrimeric G-proteins associate with microtubules during differentiation in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. FASEB J. 17: 848–859
Labbe J.-C., Maddox P. S., Salmon E. D. and Goldstein B. (2003) PAR proteins regulate microtubule dynamics at the cell cortex in C. elegans. Curr. Biol.13}: 707–
Ghosh M., Peterson Y. K., Lanier S. M. and Smrcka A. V. (2003) Receptor- and nucleotide exchange-independent mechanisms for promoting G protein subunit dissociation. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 34747–34750
Webb C. K., McCudden C. R., Willard F. S., Kimple R. J., Siderovski D. P. and Oxford G. S. (2005) D2 dopamine receptor activation of potassium channels is selectively decoupled by G-alpha-i-specific GoLoco motif peptides. J. Neurochem. in press
Tsou M.-F. B., Hayashi A. and Rose L. S. (2003) LET-99 opposes Galpha/GPR signaling to generate asymmetry for spindle positioning in response to PAR and MES-1/SRC-1 signaling. Development 130: 5717–5730
Ross E. M. and Wilkie T. M. (2000) GTPase-activating proteins for heterotrimeric G proteins: regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) and RGS-like proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 69: 795–827
Singer A. U., Waldo G. L., Harden T. K. and Sondek J. (2002) A unique fold of phospholipase C-beta mediates dimerization and interaction with G alpha q. Nat. Struct. Biol. 9: 32–36
Wang Z. and Moran M. F. (2002) Phospholipase C-gamma1: a phospholipase and guanine nucleotide exchange factor. Mol. Interv. 2: 352–355
Acknowledgement
We thank Christopher A. Johnston for critical appraisal of this review. C.R.M. and F.S.W. are postdoctoral fellows of the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada and the American Heart Association, respectively. R.J.K. acknowledges predoctoral fellowship support from the NIMH F30 MH64319. Work in the Siderovski laboratory is funded by U.S. National Institutes of Health grants GM062338 and GM065533.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 21 October 2004; received after revision 20 November 2004; accepted 30 November 2004
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCudden, C.R., Hains, M.D., Kimple, R.J. et al. G-protein signaling: back to the future. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 62, 551–577 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4462-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4462-3